| // Copyright 2013 The Flutter Authors. All rights reserved. |
| // Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be |
| // found in the LICENSE file. |
| |
| part of dart.ui; |
| |
| /// Base class for [Size] and [Offset], which are both ways to describe |
| /// a distance as a two-dimensional axis-aligned vector. |
| abstract class OffsetBase { |
| /// Abstract const constructor. This constructor enables subclasses to provide |
| /// const constructors so that they can be used in const expressions. |
| /// |
| /// The first argument sets the horizontal component, and the second the |
| /// vertical component. |
| const OffsetBase(this._dx, this._dy); |
| |
| final double _dx; |
| final double _dy; |
| |
| /// Returns true if either component is [double.infinity], and false if both |
| /// are finite (or negative infinity, or NaN). |
| /// |
| /// This is different than comparing for equality with an instance that has |
| /// _both_ components set to [double.infinity]. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [isFinite], which is true if both components are finite (and not NaN). |
| bool get isInfinite => _dx >= double.infinity || _dy >= double.infinity; |
| |
| /// Whether both components are finite (neither infinite nor NaN). |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [isInfinite], which returns true if either component is equal to |
| /// positive infinity. |
| bool get isFinite => _dx.isFinite && _dy.isFinite; |
| |
| /// Less-than operator. Compares an [Offset] or [Size] to another [Offset] or |
| /// [Size], and returns true if both the horizontal and vertical values of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand are smaller than the horizontal and vertical values |
| /// of the right-hand-side operand respectively. Returns false otherwise. |
| /// |
| /// This is a partial ordering. It is possible for two values to be neither |
| /// less, nor greater than, nor equal to, another. |
| bool operator <(OffsetBase other) => _dx < other._dx && _dy < other._dy; |
| |
| /// Less-than-or-equal-to operator. Compares an [Offset] or [Size] to another |
| /// [Offset] or [Size], and returns true if both the horizontal and vertical |
| /// values of the left-hand-side operand are smaller than or equal to the |
| /// horizontal and vertical values of the right-hand-side operand |
| /// respectively. Returns false otherwise. |
| /// |
| /// This is a partial ordering. It is possible for two values to be neither |
| /// less, nor greater than, nor equal to, another. |
| bool operator <=(OffsetBase other) => _dx <= other._dx && _dy <= other._dy; |
| |
| /// Greater-than operator. Compares an [Offset] or [Size] to another [Offset] |
| /// or [Size], and returns true if both the horizontal and vertical values of |
| /// the left-hand-side operand are bigger than the horizontal and vertical |
| /// values of the right-hand-side operand respectively. Returns false |
| /// otherwise. |
| /// |
| /// This is a partial ordering. It is possible for two values to be neither |
| /// less, nor greater than, nor equal to, another. |
| bool operator >(OffsetBase other) => _dx > other._dx && _dy > other._dy; |
| |
| /// Greater-than-or-equal-to operator. Compares an [Offset] or [Size] to |
| /// another [Offset] or [Size], and returns true if both the horizontal and |
| /// vertical values of the left-hand-side operand are bigger than or equal to |
| /// the horizontal and vertical values of the right-hand-side operand |
| /// respectively. Returns false otherwise. |
| /// |
| /// This is a partial ordering. It is possible for two values to be neither |
| /// less, nor greater than, nor equal to, another. |
| bool operator >=(OffsetBase other) => _dx >= other._dx && _dy >= other._dy; |
| |
| /// Equality operator. Compares an [Offset] or [Size] to another [Offset] or |
| /// [Size], and returns true if the horizontal and vertical values of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand are equal to the horizontal and vertical values of |
| /// the right-hand-side operand respectively. Returns false otherwise. |
| @override |
| bool operator ==(Object other) { |
| return other is OffsetBase && other._dx == _dx && other._dy == _dy; |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| int get hashCode => Object.hash(_dx, _dy); |
| |
| @override |
| String toString() => 'OffsetBase(${_dx.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ${_dy.toStringAsFixed(1)})'; |
| } |
| |
| /// An immutable 2D floating-point offset. |
| /// |
| /// Generally speaking, Offsets can be interpreted in two ways: |
| /// |
| /// 1. As representing a point in Cartesian space a specified distance from a |
| /// separately-maintained origin. For example, the top-left position of |
| /// children in the [RenderBox] protocol is typically represented as an |
| /// [Offset] from the top left of the parent box. |
| /// |
| /// 2. As a vector that can be applied to coordinates. For example, when |
| /// painting a [RenderObject], the parent is passed an [Offset] from the |
| /// screen's origin which it can add to the offsets of its children to find |
| /// the [Offset] from the screen's origin to each of the children. |
| /// |
| /// Because a particular [Offset] can be interpreted as one sense at one time |
| /// then as the other sense at a later time, the same class is used for both |
| /// senses. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [Size], which represents a vector describing the size of a rectangle. |
| class Offset extends OffsetBase { |
| /// Creates an offset. The first argument sets [dx], the horizontal component, |
| /// and the second sets [dy], the vertical component. |
| const Offset(super.dx, super.dy); |
| |
| /// Creates an offset from its [direction] and [distance]. |
| /// |
| /// The direction is in radians clockwise from the positive x-axis. |
| /// |
| /// The distance can be omitted, to create a unit vector (distance = 1.0). |
| factory Offset.fromDirection(double direction, [double distance = 1.0]) { |
| return Offset(distance * math.cos(direction), distance * math.sin(direction)); |
| } |
| |
| /// The x component of the offset. |
| /// |
| /// The y component is given by [dy]. |
| double get dx => _dx; |
| |
| /// The y component of the offset. |
| /// |
| /// The x component is given by [dx]. |
| double get dy => _dy; |
| |
| /// The magnitude of the offset. |
| /// |
| /// If you need this value to compare it to another [Offset]'s distance, |
| /// consider using [distanceSquared] instead, since it is cheaper to compute. |
| double get distance => math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy); |
| |
| /// The square of the magnitude of the offset. |
| /// |
| /// This is cheaper than computing the [distance] itself. |
| double get distanceSquared => dx * dx + dy * dy; |
| |
| /// The angle of this offset as radians clockwise from the positive x-axis, in |
| /// the range -[pi] to [pi], assuming positive values of the x-axis go to the |
| /// right and positive values of the y-axis go down. |
| /// |
| /// Zero means that [dy] is zero and [dx] is zero or positive. |
| /// |
| /// Values from zero to [pi]/2 indicate positive values of [dx] and [dy], the |
| /// bottom-right quadrant. |
| /// |
| /// Values from [pi]/2 to [pi] indicate negative values of [dx] and positive |
| /// values of [dy], the bottom-left quadrant. |
| /// |
| /// Values from zero to -[pi]/2 indicate positive values of [dx] and negative |
| /// values of [dy], the top-right quadrant. |
| /// |
| /// Values from -[pi]/2 to -[pi] indicate negative values of [dx] and [dy], |
| /// the top-left quadrant. |
| /// |
| /// When [dy] is zero and [dx] is negative, the [direction] is [pi]. |
| /// |
| /// When [dx] is zero, [direction] is [pi]/2 if [dy] is positive and -[pi]/2 |
| /// if [dy] is negative. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [distance], to compute the magnitude of the vector. |
| /// * [Canvas.rotate], which uses the same convention for its angle. |
| double get direction => math.atan2(dy, dx); |
| |
| /// An offset with zero magnitude. |
| /// |
| /// This can be used to represent the origin of a coordinate space. |
| static const Offset zero = Offset(0.0, 0.0); |
| |
| /// An offset with infinite x and y components. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [isInfinite], which checks whether either component is infinite. |
| /// * [isFinite], which checks whether both components are finite. |
| // This is included for completeness, because [Size.infinite] exists. |
| static const Offset infinite = Offset(double.infinity, double.infinity); |
| |
| /// Returns a new offset with the x component scaled by `scaleX` and the y |
| /// component scaled by `scaleY`. |
| /// |
| /// If the two scale arguments are the same, consider using the `*` operator |
| /// instead: |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// Offset a = const Offset(10.0, 10.0); |
| /// Offset b = a * 2.0; // same as: a.scale(2.0, 2.0) |
| /// ``` |
| /// |
| /// If the two arguments are -1, consider using the unary `-` operator |
| /// instead: |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// Offset a = const Offset(10.0, 10.0); |
| /// Offset b = -a; // same as: a.scale(-1.0, -1.0) |
| /// ``` |
| Offset scale(double scaleX, double scaleY) => Offset(dx * scaleX, dy * scaleY); |
| |
| /// Returns a new offset with translateX added to the x component and |
| /// translateY added to the y component. |
| /// |
| /// If the arguments come from another [Offset], consider using the `+` or `-` |
| /// operators instead: |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// Offset a = const Offset(10.0, 10.0); |
| /// Offset b = const Offset(10.0, 10.0); |
| /// Offset c = a + b; // same as: a.translate(b.dx, b.dy) |
| /// Offset d = a - b; // same as: a.translate(-b.dx, -b.dy) |
| /// ``` |
| Offset translate(double translateX, double translateY) => |
| Offset(dx + translateX, dy + translateY); |
| |
| /// Unary negation operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns an offset with the coordinates negated. |
| /// |
| /// If the [Offset] represents an arrow on a plane, this operator returns the |
| /// same arrow but pointing in the reverse direction. |
| Offset operator -() => Offset(-dx, -dy); |
| |
| /// Binary subtraction operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns an offset whose [dx] value is the left-hand-side operand's [dx] |
| /// minus the right-hand-side operand's [dx] and whose [dy] value is the |
| /// left-hand-side operand's [dy] minus the right-hand-side operand's [dy]. |
| /// |
| /// See also [translate]. |
| Offset operator -(Offset other) => Offset(dx - other.dx, dy - other.dy); |
| |
| /// Binary addition operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns an offset whose [dx] value is the sum of the [dx] values of the |
| /// two operands, and whose [dy] value is the sum of the [dy] values of the |
| /// two operands. |
| /// |
| /// See also [translate]. |
| Offset operator +(Offset other) => Offset(dx + other.dx, dy + other.dy); |
| |
| /// Multiplication operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns an offset whose coordinates are the coordinates of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand (an Offset) multiplied by the scalar |
| /// right-hand-side operand (a double). |
| /// |
| /// See also [scale]. |
| Offset operator *(double operand) => Offset(dx * operand, dy * operand); |
| |
| /// Division operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns an offset whose coordinates are the coordinates of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand (an Offset) divided by the scalar right-hand-side |
| /// operand (a double). |
| /// |
| /// See also [scale]. |
| Offset operator /(double operand) => Offset(dx / operand, dy / operand); |
| |
| /// Integer (truncating) division operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns an offset whose coordinates are the coordinates of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand (an Offset) divided by the scalar right-hand-side |
| /// operand (a double), rounded towards zero. |
| Offset operator ~/(double operand) => |
| Offset((dx ~/ operand).toDouble(), (dy ~/ operand).toDouble()); |
| |
| /// Modulo (remainder) operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns an offset whose coordinates are the remainder of dividing the |
| /// coordinates of the left-hand-side operand (an Offset) by the scalar |
| /// right-hand-side operand (a double). |
| Offset operator %(double operand) => Offset(dx % operand, dy % operand); |
| |
| /// Rectangle constructor operator. |
| /// |
| /// Combines an [Offset] and a [Size] to form a [Rect] whose top-left |
| /// coordinate is the point given by adding this offset, the left-hand-side |
| /// operand, to the origin, and whose size is the right-hand-side operand. |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// Rect myRect = Offset.zero & const Size(100.0, 100.0); |
| /// // same as: Rect.fromLTWH(0.0, 0.0, 100.0, 100.0) |
| /// ``` |
| Rect operator &(Size other) => Rect.fromLTWH(dx, dy, other.width, other.height); |
| |
| /// Linearly interpolate between two offsets. |
| /// |
| /// If either offset is null, this function interpolates from [Offset.zero]. |
| /// |
| /// The `t` argument represents position on the timeline, with 0.0 meaning |
| /// that the interpolation has not started, returning `a` (or something |
| /// equivalent to `a`), 1.0 meaning that the interpolation has finished, |
| /// returning `b` (or something equivalent to `b`), and values in between |
| /// meaning that the interpolation is at the relevant point on the timeline |
| /// between `a` and `b`. The interpolation can be extrapolated beyond 0.0 and |
| /// 1.0, so negative values and values greater than 1.0 are valid (and can |
| /// easily be generated by curves such as [Curves.elasticInOut]). |
| /// |
| /// Values for `t` are usually obtained from an [Animation<double>], such as |
| /// an [AnimationController]. |
| static Offset? lerp(Offset? a, Offset? b, double t) { |
| if (b == null) { |
| if (a == null) { |
| return null; |
| } else { |
| return a * (1.0 - t); |
| } |
| } else { |
| if (a == null) { |
| return b * t; |
| } else { |
| return Offset(_lerpDouble(a.dx, b.dx, t), _lerpDouble(a.dy, b.dy, t)); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| |
| /// Compares two Offsets for equality. |
| @override |
| bool operator ==(Object other) { |
| return other is Offset && other.dx == dx && other.dy == dy; |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| int get hashCode => Object.hash(dx, dy); |
| |
| @override |
| String toString() => 'Offset(${dx.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ${dy.toStringAsFixed(1)})'; |
| } |
| |
| /// Holds a 2D floating-point size. |
| /// |
| /// You can think of this as an [Offset] from the origin. |
| class Size extends OffsetBase { |
| /// Creates a [Size] with the given [width] and [height]. |
| const Size(super.width, super.height); |
| |
| /// Creates an instance of [Size] that has the same values as another. |
| // Used by the rendering library's _DebugSize hack. |
| Size.copy(Size source) : super(source.width, source.height); |
| |
| /// Creates a square [Size] whose [width] and [height] are the given dimension. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [Size.fromRadius], which is more convenient when the available size |
| /// is the radius of a circle. |
| const Size.square(double dimension) : super(dimension, dimension); |
| |
| /// Creates a [Size] with the given [width] and an infinite [height]. |
| const Size.fromWidth(double width) : super(width, double.infinity); |
| |
| /// Creates a [Size] with the given [height] and an infinite [width]. |
| const Size.fromHeight(double height) : super(double.infinity, height); |
| |
| /// Creates a square [Size] whose [width] and [height] are twice the given |
| /// dimension. |
| /// |
| /// This is a square that contains a circle with the given radius. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [Size.square], which creates a square with the given dimension. |
| const Size.fromRadius(double radius) : super(radius * 2.0, radius * 2.0); |
| |
| /// The horizontal extent of this size. |
| double get width => _dx; |
| |
| /// The vertical extent of this size. |
| double get height => _dy; |
| |
| /// The aspect ratio of this size. |
| /// |
| /// This returns the [width] divided by the [height]. |
| /// |
| /// If the [width] is zero, the result will be zero. If the [height] is zero |
| /// (and the [width] is not), the result will be [double.infinity] or |
| /// [double.negativeInfinity] as determined by the sign of [width]. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [AspectRatio], a widget for giving a child widget a specific aspect |
| /// ratio. |
| /// * [FittedBox], a widget that (in most modes) attempts to maintain a |
| /// child widget's aspect ratio while changing its size. |
| double get aspectRatio { |
| if (height != 0.0) { |
| return width / height; |
| } |
| if (width > 0.0) { |
| return double.infinity; |
| } |
| if (width < 0.0) { |
| return double.negativeInfinity; |
| } |
| return 0.0; |
| } |
| |
| /// An empty size, one with a zero width and a zero height. |
| static const Size zero = Size(0.0, 0.0); |
| |
| /// A size whose [width] and [height] are infinite. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [isInfinite], which checks whether either dimension is infinite. |
| /// * [isFinite], which checks whether both dimensions are finite. |
| static const Size infinite = Size(double.infinity, double.infinity); |
| |
| /// Whether this size encloses a non-zero area. |
| /// |
| /// Negative areas are considered empty. |
| bool get isEmpty => width <= 0.0 || height <= 0.0; |
| |
| /// Binary subtraction operator for [Size]. |
| /// |
| /// Subtracting a [Size] from a [Size] returns the [Offset] that describes how |
| /// much bigger the left-hand-side operand is than the right-hand-side |
| /// operand. Adding that resulting [Offset] to the [Size] that was the |
| /// right-hand-side operand would return a [Size] equal to the [Size] that was |
| /// the left-hand-side operand. (i.e. if `sizeA - sizeB -> offsetA`, then |
| /// `offsetA + sizeB -> sizeA`) |
| /// |
| /// Subtracting an [Offset] from a [Size] returns the [Size] that is smaller than |
| /// the [Size] operand by the difference given by the [Offset] operand. In other |
| /// words, the returned [Size] has a [width] consisting of the [width] of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand minus the [Offset.dx] dimension of the |
| /// right-hand-side operand, and a [height] consisting of the [height] of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand minus the [Offset.dy] dimension of the |
| /// right-hand-side operand. |
| OffsetBase operator -(OffsetBase other) { |
| if (other is Size) { |
| return Offset(width - other.width, height - other.height); |
| } |
| if (other is Offset) { |
| return Size(width - other.dx, height - other.dy); |
| } |
| throw ArgumentError(other); |
| } |
| |
| /// Binary addition operator for adding an [Offset] to a [Size]. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a [Size] whose [width] is the sum of the [width] of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand, a [Size], and the [Offset.dx] dimension of the |
| /// right-hand-side operand, an [Offset], and whose [height] is the sum of the |
| /// [height] of the left-hand-side operand and the [Offset.dy] dimension of |
| /// the right-hand-side operand. |
| Size operator +(Offset other) => Size(width + other.dx, height + other.dy); |
| |
| /// Multiplication operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a [Size] whose dimensions are the dimensions of the left-hand-side |
| /// operand (a [Size]) multiplied by the scalar right-hand-side operand (a |
| /// [double]). |
| Size operator *(double operand) => Size(width * operand, height * operand); |
| |
| /// Division operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a [Size] whose dimensions are the dimensions of the left-hand-side |
| /// operand (a [Size]) divided by the scalar right-hand-side operand (a |
| /// [double]). |
| Size operator /(double operand) => Size(width / operand, height / operand); |
| |
| /// Integer (truncating) division operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a [Size] whose dimensions are the dimensions of the left-hand-side |
| /// operand (a [Size]) divided by the scalar right-hand-side operand (a |
| /// [double]), rounded towards zero. |
| Size operator ~/(double operand) => |
| Size((width ~/ operand).toDouble(), (height ~/ operand).toDouble()); |
| |
| /// Modulo (remainder) operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a [Size] whose dimensions are the remainder of dividing the |
| /// left-hand-side operand (a [Size]) by the scalar right-hand-side operand (a |
| /// [double]). |
| Size operator %(double operand) => Size(width % operand, height % operand); |
| |
| /// The lesser of the magnitudes of the [width] and the [height]. |
| double get shortestSide => math.min(width.abs(), height.abs()); |
| |
| /// The greater of the magnitudes of the [width] and the [height]. |
| double get longestSide => math.max(width.abs(), height.abs()); |
| |
| // Convenience methods that do the equivalent of calling the similarly named |
| // methods on a Rect constructed from the given origin and this size. |
| |
| /// The offset to the intersection of the top and left edges of the rectangle |
| /// described by the given [Offset] (which is interpreted as the top-left corner) |
| /// and this [Size]. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Rect.topLeft]. |
| Offset topLeft(Offset origin) => origin; |
| |
| /// The offset to the center of the top edge of the rectangle described by the |
| /// given offset (which is interpreted as the top-left corner) and this size. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Rect.topCenter]. |
| Offset topCenter(Offset origin) => Offset(origin.dx + width / 2.0, origin.dy); |
| |
| /// The offset to the intersection of the top and right edges of the rectangle |
| /// described by the given offset (which is interpreted as the top-left corner) |
| /// and this size. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Rect.topRight]. |
| Offset topRight(Offset origin) => Offset(origin.dx + width, origin.dy); |
| |
| /// The offset to the center of the left edge of the rectangle described by the |
| /// given offset (which is interpreted as the top-left corner) and this size. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Rect.centerLeft]. |
| Offset centerLeft(Offset origin) => Offset(origin.dx, origin.dy + height / 2.0); |
| |
| /// The offset to the point halfway between the left and right and the top and |
| /// bottom edges of the rectangle described by the given offset (which is |
| /// interpreted as the top-left corner) and this size. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Rect.center]. |
| Offset center(Offset origin) => Offset(origin.dx + width / 2.0, origin.dy + height / 2.0); |
| |
| /// The offset to the center of the right edge of the rectangle described by the |
| /// given offset (which is interpreted as the top-left corner) and this size. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Rect.centerRight]. |
| Offset centerRight(Offset origin) => Offset(origin.dx + width, origin.dy + height / 2.0); |
| |
| /// The offset to the intersection of the bottom and left edges of the |
| /// rectangle described by the given offset (which is interpreted as the |
| /// top-left corner) and this size. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Rect.bottomLeft]. |
| Offset bottomLeft(Offset origin) => Offset(origin.dx, origin.dy + height); |
| |
| /// The offset to the center of the bottom edge of the rectangle described by |
| /// the given offset (which is interpreted as the top-left corner) and this |
| /// size. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Rect.bottomCenter]. |
| Offset bottomCenter(Offset origin) => Offset(origin.dx + width / 2.0, origin.dy + height); |
| |
| /// The offset to the intersection of the bottom and right edges of the |
| /// rectangle described by the given offset (which is interpreted as the |
| /// top-left corner) and this size. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Rect.bottomRight]. |
| Offset bottomRight(Offset origin) => Offset(origin.dx + width, origin.dy + height); |
| |
| /// Whether the point specified by the given offset (which is assumed to be |
| /// relative to the top left of the size) lies between the left and right and |
| /// the top and bottom edges of a rectangle of this size. |
| /// |
| /// Rectangles include their top and left edges but exclude their bottom and |
| /// right edges. |
| bool contains(Offset offset) { |
| return offset.dx >= 0.0 && offset.dx < width && offset.dy >= 0.0 && offset.dy < height; |
| } |
| |
| /// A [Size] with the [width] and [height] swapped. |
| Size get flipped => Size(height, width); |
| |
| /// Linearly interpolate between two sizes |
| /// |
| /// If either size is null, this function interpolates from [Size.zero]. |
| /// |
| /// The `t` argument represents position on the timeline, with 0.0 meaning |
| /// that the interpolation has not started, returning `a` (or something |
| /// equivalent to `a`), 1.0 meaning that the interpolation has finished, |
| /// returning `b` (or something equivalent to `b`), and values in between |
| /// meaning that the interpolation is at the relevant point on the timeline |
| /// between `a` and `b`. The interpolation can be extrapolated beyond 0.0 and |
| /// 1.0, so negative values and values greater than 1.0 are valid (and can |
| /// easily be generated by curves such as [Curves.elasticInOut]). |
| /// |
| /// Values for `t` are usually obtained from an [Animation<double>], such as |
| /// an [AnimationController]. |
| static Size? lerp(Size? a, Size? b, double t) { |
| if (b == null) { |
| if (a == null) { |
| return null; |
| } else { |
| return a * (1.0 - t); |
| } |
| } else { |
| if (a == null) { |
| return b * t; |
| } else { |
| return Size(_lerpDouble(a.width, b.width, t), _lerpDouble(a.height, b.height, t)); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| |
| /// Compares two Sizes for equality. |
| // We don't compare the runtimeType because of _DebugSize in the framework. |
| @override |
| bool operator ==(Object other) { |
| return other is Size && other._dx == _dx && other._dy == _dy; |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| int get hashCode => Object.hash(_dx, _dy); |
| |
| @override |
| String toString() => 'Size(${width.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ${height.toStringAsFixed(1)})'; |
| } |
| |
| /// An immutable, 2D, axis-aligned, floating-point rectangle whose coordinates |
| /// are relative to a given origin. |
| /// |
| /// A Rect can be created with one of its constructors or from an [Offset] and a |
| /// [Size] using the `&` operator: |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// Rect myRect = const Offset(1.0, 2.0) & const Size(3.0, 4.0); |
| /// ``` |
| class Rect { |
| /// Construct a rectangle from its left, top, right, and bottom edges. |
| /// |
| /// 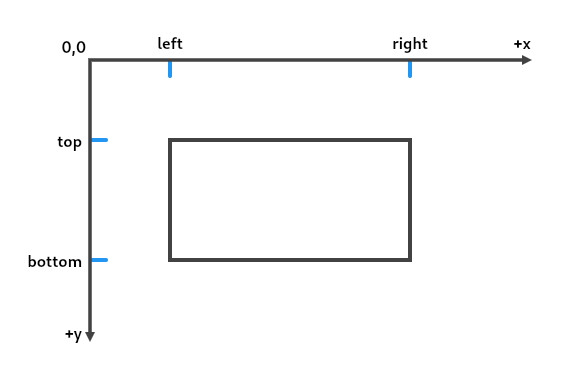 |
| ///  |
| const Rect.fromLTRB(this.left, this.top, this.right, this.bottom); |
| |
| /// Construct a rectangle from its left and top edges, its width, and its |
| /// height. |
| /// |
| /// To construct a [Rect] from an [Offset] and a [Size], you can use the |
| /// rectangle constructor operator `&`. See [Offset.&]. |
| /// |
| /// 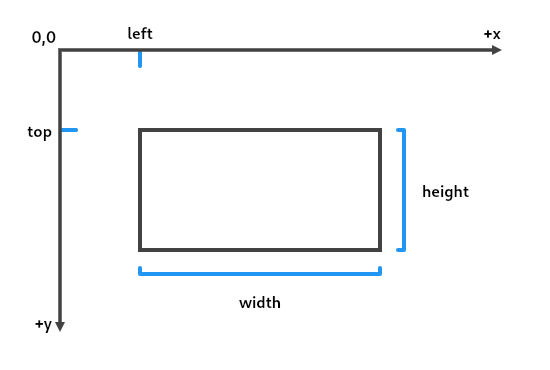 |
| ///  |
| const Rect.fromLTWH(double left, double top, double width, double height) |
| : this.fromLTRB(left, top, left + width, top + height); |
| |
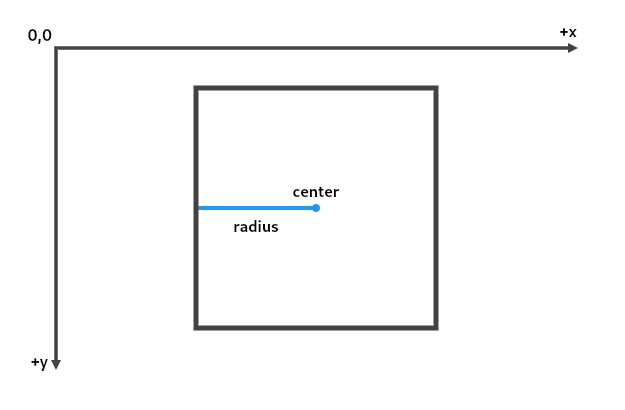
| /// Construct a rectangle that bounds the given circle. |
| /// |
| /// The `center` argument is assumed to be an offset from the origin. |
| /// |
| ///  |
| ///  |
| Rect.fromCircle({required Offset center, required double radius}) |
| : this.fromCenter(center: center, width: radius * 2, height: radius * 2); |
| |
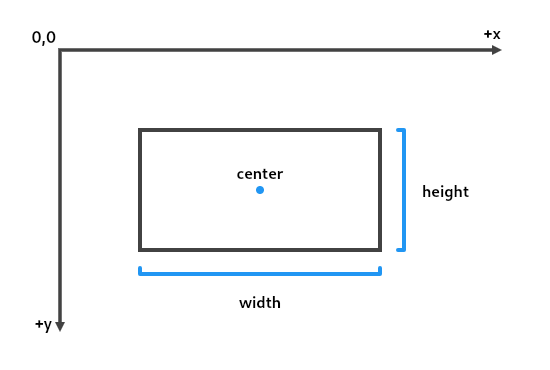
| /// Constructs a rectangle from its center point, width, and height. |
| /// |
| /// The `center` argument is assumed to be an offset from the origin. |
| /// |
| ///  |
| ///  |
| Rect.fromCenter({required Offset center, required double width, required double height}) |
| : this.fromLTRB( |
| center.dx - width / 2, |
| center.dy - height / 2, |
| center.dx + width / 2, |
| center.dy + height / 2, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct the smallest rectangle that encloses the given offsets, treating |
| /// them as vectors from the origin. |
| /// |
| /// 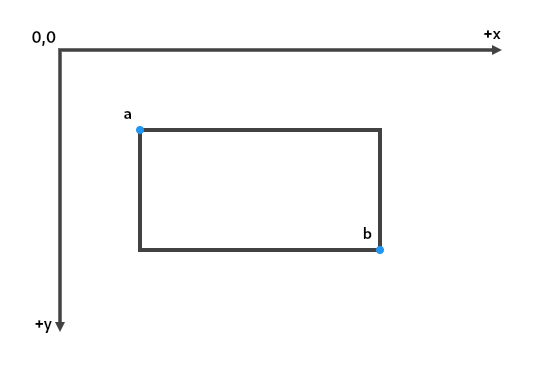 |
| ///  |
| Rect.fromPoints(Offset a, Offset b) |
| : this.fromLTRB( |
| math.min(a.dx, b.dx), |
| math.min(a.dy, b.dy), |
| math.max(a.dx, b.dx), |
| math.max(a.dy, b.dy), |
| ); |
| |
| Float32List _getValue32() { |
| final Float32List result = Float32List(4); |
| result[0] = left; |
| result[1] = top; |
| result[2] = right; |
| result[3] = bottom; |
| return result; |
| } |
| |
| /// The offset of the left edge of this rectangle from the x axis. |
| final double left; |
| |
| /// The offset of the top edge of this rectangle from the y axis. |
| final double top; |
| |
| /// The offset of the right edge of this rectangle from the x axis. |
| final double right; |
| |
| /// The offset of the bottom edge of this rectangle from the y axis. |
| final double bottom; |
| |
| /// The distance between the left and right edges of this rectangle. |
| double get width => right - left; |
| |
| /// The distance between the top and bottom edges of this rectangle. |
| double get height => bottom - top; |
| |
| /// The distance between the upper-left corner and the lower-right corner of |
| /// this rectangle. |
| Size get size => Size(width, height); |
| |
| /// Whether any of the dimensions are `NaN`. |
| bool get hasNaN => left.isNaN || top.isNaN || right.isNaN || bottom.isNaN; |
| |
| /// A rectangle with left, top, right, and bottom edges all at zero. |
| static const Rect zero = Rect.fromLTRB(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); |
| |
| static const double _giantScalar = 1.0E+9; // matches kGiantRect from layer.h |
| |
| /// A rectangle that covers the entire coordinate space. |
| /// |
| /// This covers the space from -1e9,-1e9 to 1e9,1e9. |
| /// This is the space over which graphics operations are valid. |
| static const Rect largest = Rect.fromLTRB( |
| -_giantScalar, |
| -_giantScalar, |
| _giantScalar, |
| _giantScalar, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Whether any of the coordinates of this rectangle are equal to positive infinity. |
| // included for consistency with Offset and Size |
| bool get isInfinite { |
| return left >= double.infinity || |
| top >= double.infinity || |
| right >= double.infinity || |
| bottom >= double.infinity; |
| } |
| |
| /// Whether all coordinates of this rectangle are finite. |
| bool get isFinite => left.isFinite && top.isFinite && right.isFinite && bottom.isFinite; |
| |
| /// Whether this rectangle encloses a non-zero area. Negative areas are |
| /// considered empty. |
| bool get isEmpty => left >= right || top >= bottom; |
| |
| /// Returns a new rectangle translated by the given offset. |
| /// |
| /// To translate a rectangle by separate x and y components rather than by an |
| /// [Offset], consider [translate]. |
| Rect shift(Offset offset) { |
| return Rect.fromLTRB(left + offset.dx, top + offset.dy, right + offset.dx, bottom + offset.dy); |
| } |
| |
| /// Returns a new rectangle with translateX added to the x components and |
| /// translateY added to the y components. |
| /// |
| /// To translate a rectangle by an [Offset] rather than by separate x and y |
| /// components, consider [shift]. |
| Rect translate(double translateX, double translateY) { |
| return Rect.fromLTRB( |
| left + translateX, |
| top + translateY, |
| right + translateX, |
| bottom + translateY, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Returns a new rectangle with edges moved outwards by the given delta. |
| Rect inflate(double delta) { |
| return Rect.fromLTRB(left - delta, top - delta, right + delta, bottom + delta); |
| } |
| |
| /// Returns a new rectangle with edges moved inwards by the given delta. |
| Rect deflate(double delta) => inflate(-delta); |
| |
| /// Returns a new rectangle that is the intersection of the given |
| /// rectangle and this rectangle. The two rectangles must overlap |
| /// for this to be meaningful. If the two rectangles do not overlap, |
| /// then the resulting Rect will have a negative width or height. |
| Rect intersect(Rect other) { |
| return Rect.fromLTRB( |
| math.max(left, other.left), |
| math.max(top, other.top), |
| math.min(right, other.right), |
| math.min(bottom, other.bottom), |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Returns a new rectangle which is the bounding box containing this |
| /// rectangle and the given rectangle. |
| Rect expandToInclude(Rect other) { |
| return Rect.fromLTRB( |
| math.min(left, other.left), |
| math.min(top, other.top), |
| math.max(right, other.right), |
| math.max(bottom, other.bottom), |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Whether `other` has a nonzero area of overlap with this rectangle. |
| bool overlaps(Rect other) { |
| if (right <= other.left || other.right <= left) { |
| return false; |
| } |
| if (bottom <= other.top || other.bottom <= top) { |
| return false; |
| } |
| return true; |
| } |
| |
| /// The lesser of the magnitudes of the [width] and the [height] of this |
| /// rectangle. |
| double get shortestSide => math.min(width.abs(), height.abs()); |
| |
| /// The greater of the magnitudes of the [width] and the [height] of this |
| /// rectangle. |
| double get longestSide => math.max(width.abs(), height.abs()); |
| |
| /// The offset to the intersection of the top and left edges of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Size.topLeft]. |
| Offset get topLeft => Offset(left, top); |
| |
| /// The offset to the center of the top edge of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Size.topCenter]. |
| Offset get topCenter => Offset(left + width / 2.0, top); |
| |
| /// The offset to the intersection of the top and right edges of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Size.topRight]. |
| Offset get topRight => Offset(right, top); |
| |
| /// The offset to the center of the left edge of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Size.centerLeft]. |
| Offset get centerLeft => Offset(left, top + height / 2.0); |
| |
| /// The offset to the point halfway between the left and right and the top and |
| /// bottom edges of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Size.center]. |
| Offset get center => Offset(left + width / 2.0, top + height / 2.0); |
| |
| /// The offset to the center of the right edge of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Size.centerRight]. |
| Offset get centerRight => Offset(right, top + height / 2.0); |
| |
| /// The offset to the intersection of the bottom and left edges of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Size.bottomLeft]. |
| Offset get bottomLeft => Offset(left, bottom); |
| |
| /// The offset to the center of the bottom edge of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Size.bottomCenter]. |
| Offset get bottomCenter => Offset(left + width / 2.0, bottom); |
| |
| /// The offset to the intersection of the bottom and right edges of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// See also [Size.bottomRight]. |
| Offset get bottomRight => Offset(right, bottom); |
| |
| /// Whether the point specified by the given offset (which is assumed to be |
| /// relative to the origin) lies between the left and right and the top and |
| /// bottom edges of this rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// Rectangles include their top and left edges but exclude their bottom and |
| /// right edges. |
| bool contains(Offset offset) { |
| return offset.dx >= left && offset.dx < right && offset.dy >= top && offset.dy < bottom; |
| } |
| |
| /// Linearly interpolate between two rectangles. |
| /// |
| /// If either rect is null, [Rect.zero] is used as a substitute. |
| /// |
| /// The `t` argument represents position on the timeline, with 0.0 meaning |
| /// that the interpolation has not started, returning `a` (or something |
| /// equivalent to `a`), 1.0 meaning that the interpolation has finished, |
| /// returning `b` (or something equivalent to `b`), and values in between |
| /// meaning that the interpolation is at the relevant point on the timeline |
| /// between `a` and `b`. The interpolation can be extrapolated beyond 0.0 and |
| /// 1.0, so negative values and values greater than 1.0 are valid (and can |
| /// easily be generated by curves such as [Curves.elasticInOut]). |
| /// |
| /// Values for `t` are usually obtained from an [Animation<double>], such as |
| /// an [AnimationController]. |
| static Rect? lerp(Rect? a, Rect? b, double t) { |
| if (b == null) { |
| if (a == null) { |
| return null; |
| } else { |
| final double k = 1.0 - t; |
| return Rect.fromLTRB(a.left * k, a.top * k, a.right * k, a.bottom * k); |
| } |
| } else { |
| if (a == null) { |
| return Rect.fromLTRB(b.left * t, b.top * t, b.right * t, b.bottom * t); |
| } else { |
| return Rect.fromLTRB( |
| _lerpDouble(a.left, b.left, t), |
| _lerpDouble(a.top, b.top, t), |
| _lerpDouble(a.right, b.right, t), |
| _lerpDouble(a.bottom, b.bottom, t), |
| ); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| bool operator ==(Object other) { |
| if (identical(this, other)) { |
| return true; |
| } |
| if (runtimeType != other.runtimeType) { |
| return false; |
| } |
| return other is Rect && |
| other.left == left && |
| other.top == top && |
| other.right == right && |
| other.bottom == bottom; |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| int get hashCode => Object.hash(left, top, right, bottom); |
| |
| @override |
| String toString() => |
| 'Rect.fromLTRB(${left.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ${top.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ${right.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ${bottom.toStringAsFixed(1)})'; |
| } |
| |
| /// A radius for either circular or elliptical shapes. |
| class Radius { |
| /// Constructs a circular radius. [x] and [y] will have the same radius value. |
| /// |
| /// 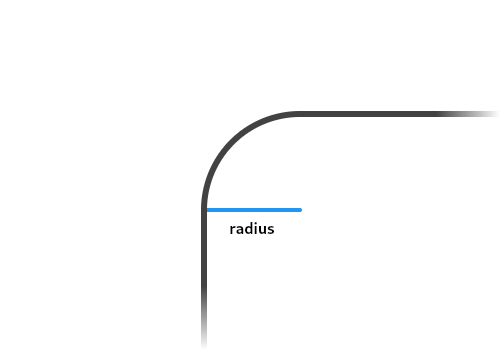 |
| ///  |
| const Radius.circular(double radius) : this.elliptical(radius, radius); |
| |
| /// Constructs an elliptical radius with the given radii. |
| /// |
| ///  |
| ///  |
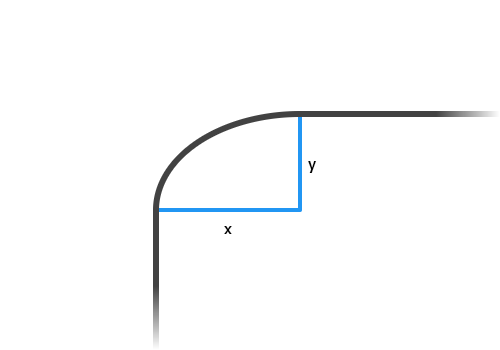
| const Radius.elliptical(this.x, this.y); |
| |
| /// The radius value on the horizontal axis. |
| final double x; |
| |
| /// The radius value on the vertical axis. |
| final double y; |
| |
| /// A radius with [x] and [y] values set to zero. |
| /// |
| /// You can use [Radius.zero] with [RRect] or [RSuperellipse] to have |
| /// right-angle corners. |
| static const Radius zero = Radius.circular(0.0); |
| |
| /// Returns this [Radius], with values clamped to the given min and max |
| /// [Radius] values. |
| /// |
| /// The `min` value defaults to `Radius.circular(-double.infinity)`, and |
| /// the `max` value defaults to `Radius.circular(double.infinity)`. |
| Radius clamp({Radius? minimum, Radius? maximum}) { |
| minimum ??= const Radius.circular(-double.infinity); |
| maximum ??= const Radius.circular(double.infinity); |
| return Radius.elliptical( |
| clampDouble(x, minimum.x, maximum.x), |
| clampDouble(y, minimum.y, maximum.y), |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Returns this [Radius], with values clamped to the given min and max |
| /// values in each dimension |
| /// |
| /// The `minimumX` and `minimumY` values default to `-double.infinity`, and |
| /// the `maximumX` and `maximumY` values default to `double.infinity`. |
| Radius clampValues({double? minimumX, double? minimumY, double? maximumX, double? maximumY}) { |
| return Radius.elliptical( |
| clampDouble(x, minimumX ?? -double.infinity, maximumX ?? double.infinity), |
| clampDouble(y, minimumY ?? -double.infinity, maximumY ?? double.infinity), |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Unary negation operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a Radius with the distances negated. |
| /// |
| /// Radiuses with negative values aren't geometrically meaningful, but could |
| /// occur as part of expressions. For example, negating a radius of one pixel |
| /// and then adding the result to another radius is equivalent to subtracting |
| /// a radius of one pixel from the other. |
| Radius operator -() => Radius.elliptical(-x, -y); |
| |
| /// Binary subtraction operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a radius whose [x] value is the left-hand-side operand's [x] |
| /// minus the right-hand-side operand's [x] and whose [y] value is the |
| /// left-hand-side operand's [y] minus the right-hand-side operand's [y]. |
| Radius operator -(Radius other) => Radius.elliptical(x - other.x, y - other.y); |
| |
| /// Binary addition operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a radius whose [x] value is the sum of the [x] values of the |
| /// two operands, and whose [y] value is the sum of the [y] values of the |
| /// two operands. |
| Radius operator +(Radius other) => Radius.elliptical(x + other.x, y + other.y); |
| |
| /// Multiplication operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a radius whose coordinates are the coordinates of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand (a radius) multiplied by the scalar |
| /// right-hand-side operand (a double). |
| Radius operator *(double operand) => Radius.elliptical(x * operand, y * operand); |
| |
| /// Division operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a radius whose coordinates are the coordinates of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand (a radius) divided by the scalar right-hand-side |
| /// operand (a double). |
| Radius operator /(double operand) => Radius.elliptical(x / operand, y / operand); |
| |
| /// Integer (truncating) division operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a radius whose coordinates are the coordinates of the |
| /// left-hand-side operand (a radius) divided by the scalar right-hand-side |
| /// operand (a double), rounded towards zero. |
| Radius operator ~/(double operand) => |
| Radius.elliptical((x ~/ operand).toDouble(), (y ~/ operand).toDouble()); |
| |
| /// Modulo (remainder) operator. |
| /// |
| /// Returns a radius whose coordinates are the remainder of dividing the |
| /// coordinates of the left-hand-side operand (a radius) by the scalar |
| /// right-hand-side operand (a double). |
| Radius operator %(double operand) => Radius.elliptical(x % operand, y % operand); |
| |
| /// Linearly interpolate between two radii. |
| /// |
| /// If either is null, this function substitutes [Radius.zero] instead. |
| /// |
| /// The `t` argument represents position on the timeline, with 0.0 meaning |
| /// that the interpolation has not started, returning `a` (or something |
| /// equivalent to `a`), 1.0 meaning that the interpolation has finished, |
| /// returning `b` (or something equivalent to `b`), and values in between |
| /// meaning that the interpolation is at the relevant point on the timeline |
| /// between `a` and `b`. The interpolation can be extrapolated beyond 0.0 and |
| /// 1.0, so negative values and values greater than 1.0 are valid (and can |
| /// easily be generated by curves such as [Curves.elasticInOut]). |
| /// |
| /// Values for `t` are usually obtained from an [Animation<double>], such as |
| /// an [AnimationController]. |
| static Radius? lerp(Radius? a, Radius? b, double t) { |
| if (b == null) { |
| if (a == null) { |
| return null; |
| } else { |
| final double k = 1.0 - t; |
| return Radius.elliptical(a.x * k, a.y * k); |
| } |
| } else { |
| if (a == null) { |
| return Radius.elliptical(b.x * t, b.y * t); |
| } else { |
| return Radius.elliptical(_lerpDouble(a.x, b.x, t), _lerpDouble(a.y, b.y, t)); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| bool operator ==(Object other) { |
| if (identical(this, other)) { |
| return true; |
| } |
| if (runtimeType != other.runtimeType) { |
| return false; |
| } |
| |
| return other is Radius && other.x == x && other.y == y; |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| int get hashCode => Object.hash(x, y); |
| |
| @override |
| String toString() { |
| return x == y |
| ? 'Radius.circular(${x.toStringAsFixed(1)})' |
| : 'Radius.elliptical(${x.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ' |
| '${y.toStringAsFixed(1)})'; |
| } |
| } |
| |
| // The common base class for `RRect` and `RSuperellipse`. |
| abstract class _RRectLike<T extends _RRectLike<T>> { |
| const _RRectLike({ |
| required this.left, |
| required this.top, |
| required this.right, |
| required this.bottom, |
| required this.tlRadiusX, |
| required this.tlRadiusY, |
| required this.trRadiusX, |
| required this.trRadiusY, |
| required this.brRadiusX, |
| required this.brRadiusY, |
| required this.blRadiusX, |
| required this.blRadiusY, |
| }) : assert(tlRadiusX >= 0), |
| assert(tlRadiusY >= 0), |
| assert(trRadiusX >= 0), |
| assert(trRadiusY >= 0), |
| assert(brRadiusX >= 0), |
| assert(brRadiusY >= 0), |
| assert(blRadiusX >= 0), |
| assert(blRadiusY >= 0); |
| |
| // Implemented by a subclass to return an object constructed with the given |
| // parameters. |
| // |
| // Used by various methods that construct an object of the same shape. |
| T _create({ |
| required double left, |
| required double top, |
| required double right, |
| required double bottom, |
| required double tlRadiusX, |
| required double tlRadiusY, |
| required double trRadiusX, |
| required double trRadiusY, |
| required double brRadiusX, |
| required double brRadiusY, |
| required double blRadiusX, |
| required double blRadiusY, |
| }); |
| |
| /// The offset of the left edge of this rectangle from the x axis. |
| final double left; |
| |
| /// The offset of the top edge of this rectangle from the y axis. |
| final double top; |
| |
| /// The offset of the right edge of this rectangle from the x axis. |
| final double right; |
| |
| /// The offset of the bottom edge of this rectangle from the y axis. |
| final double bottom; |
| |
| /// The top-left horizontal radius. |
| final double tlRadiusX; |
| |
| /// The top-left vertical radius. |
| final double tlRadiusY; |
| |
| /// The top-left [Radius]. |
| Radius get tlRadius => Radius.elliptical(tlRadiusX, tlRadiusY); |
| |
| /// The top-right horizontal radius. |
| final double trRadiusX; |
| |
| /// The top-right vertical radius. |
| final double trRadiusY; |
| |
| /// The top-right [Radius]. |
| Radius get trRadius => Radius.elliptical(trRadiusX, trRadiusY); |
| |
| /// The bottom-right horizontal radius. |
| final double brRadiusX; |
| |
| /// The bottom-right vertical radius. |
| final double brRadiusY; |
| |
| /// The bottom-right [Radius]. |
| Radius get brRadius => Radius.elliptical(brRadiusX, brRadiusY); |
| |
| /// The bottom-left horizontal radius. |
| final double blRadiusX; |
| |
| /// The bottom-left vertical radius. |
| final double blRadiusY; |
| |
| /// The bottom-left [Radius]. |
| Radius get blRadius => Radius.elliptical(blRadiusX, blRadiusY); |
| |
| /// Returns a clone translated by the given offset. |
| T shift(Offset offset) { |
| return _create( |
| left: left + offset.dx, |
| top: top + offset.dy, |
| right: right + offset.dx, |
| bottom: bottom + offset.dy, |
| tlRadiusX: tlRadiusX, |
| tlRadiusY: tlRadiusY, |
| trRadiusX: trRadiusX, |
| trRadiusY: trRadiusY, |
| blRadiusX: blRadiusX, |
| blRadiusY: blRadiusY, |
| brRadiusX: brRadiusX, |
| brRadiusY: brRadiusY, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Returns a clone with edges and radii moved outwards by the given |
| /// delta. |
| T inflate(double delta) { |
| return _create( |
| left: left - delta, |
| top: top - delta, |
| right: right + delta, |
| bottom: bottom + delta, |
| tlRadiusX: math.max(0, tlRadiusX + delta), |
| tlRadiusY: math.max(0, tlRadiusY + delta), |
| trRadiusX: math.max(0, trRadiusX + delta), |
| trRadiusY: math.max(0, trRadiusY + delta), |
| blRadiusX: math.max(0, blRadiusX + delta), |
| blRadiusY: math.max(0, blRadiusY + delta), |
| brRadiusX: math.max(0, brRadiusX + delta), |
| brRadiusY: math.max(0, brRadiusY + delta), |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Returns a clone with edges and radii moved inwards by the given delta. |
| T deflate(double delta) => inflate(-delta); |
| |
| /// The distance between the left and right edges of this rectangle. |
| double get width => right - left; |
| |
| /// The distance between the top and bottom edges of this rectangle. |
| double get height => bottom - top; |
| |
| /// The bounding box of this rounded rectangle (the rectangle with no rounded corners). |
| Rect get outerRect => Rect.fromLTRB(left, top, right, bottom); |
| |
| /// The non-rounded rectangle that is constrained by the smaller of the two |
| /// diagonals, with each diagonal traveling through the middle of the curve |
| /// corners. The middle of a corner is the intersection of the curve with its |
| /// respective quadrant bisector. |
| Rect get safeInnerRect { |
| const double kInsetFactor = 0.29289321881; // 1-cos(pi/4) |
| |
| final double leftRadius = math.max(blRadiusX, tlRadiusX); |
| final double topRadius = math.max(tlRadiusY, trRadiusY); |
| final double rightRadius = math.max(trRadiusX, brRadiusX); |
| final double bottomRadius = math.max(brRadiusY, blRadiusY); |
| |
| return Rect.fromLTRB( |
| left + leftRadius * kInsetFactor, |
| top + topRadius * kInsetFactor, |
| right - rightRadius * kInsetFactor, |
| bottom - bottomRadius * kInsetFactor, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// The rectangle that would be formed using the axis-aligned intersection of |
| /// the sides of the rectangle, i.e., the rectangle formed from the |
| /// inner-most centers of the ellipses that form the corners. This is the |
| /// intersection of the [wideMiddleRect] and the [tallMiddleRect]. If any of |
| /// the intersections are void, the resulting [Rect] will have negative width |
| /// or height. |
| Rect get middleRect { |
| final double leftRadius = math.max(blRadiusX, tlRadiusX); |
| final double topRadius = math.max(tlRadiusY, trRadiusY); |
| final double rightRadius = math.max(trRadiusX, brRadiusX); |
| final double bottomRadius = math.max(brRadiusY, blRadiusY); |
| return Rect.fromLTRB( |
| left + leftRadius, |
| top + topRadius, |
| right - rightRadius, |
| bottom - bottomRadius, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// The biggest rectangle that is entirely inside the rounded rectangle and |
| /// has the full width of the rounded rectangle. If the rounded rectangle does |
| /// not have an axis-aligned intersection of its left and right side, the |
| /// resulting [Rect] will have negative width or height. |
| Rect get wideMiddleRect { |
| final double topRadius = math.max(tlRadiusY, trRadiusY); |
| final double bottomRadius = math.max(brRadiusY, blRadiusY); |
| return Rect.fromLTRB(left, top + topRadius, right, bottom - bottomRadius); |
| } |
| |
| /// The biggest rectangle that is entirely inside the rounded rectangle and |
| /// has the full height of the rounded rectangle. If the rounded rectangle |
| /// does not have an axis-aligned intersection of its top and bottom side, the |
| /// resulting [Rect] will have negative width or height. |
| Rect get tallMiddleRect { |
| final double leftRadius = math.max(blRadiusX, tlRadiusX); |
| final double rightRadius = math.max(trRadiusX, brRadiusX); |
| return Rect.fromLTRB(left + leftRadius, top, right - rightRadius, bottom); |
| } |
| |
| /// Whether this rounded rectangle encloses a non-zero area. |
| /// Negative areas are considered empty. |
| bool get isEmpty => left >= right || top >= bottom; |
| |
| /// Whether all coordinates of this rounded rectangle are finite. |
| bool get isFinite => left.isFinite && top.isFinite && right.isFinite && bottom.isFinite; |
| |
| /// Whether this rounded rectangle is a simple rectangle with zero |
| /// corner radii. |
| bool get isRect { |
| return (tlRadiusX == 0.0 || tlRadiusY == 0.0) && |
| (trRadiusX == 0.0 || trRadiusY == 0.0) && |
| (blRadiusX == 0.0 || blRadiusY == 0.0) && |
| (brRadiusX == 0.0 || brRadiusY == 0.0); |
| } |
| |
| /// Whether this rounded rectangle has a side with no straight section. |
| bool get isStadium { |
| return tlRadius == trRadius && |
| trRadius == brRadius && |
| brRadius == blRadius && |
| (width <= 2.0 * tlRadiusX || height <= 2.0 * tlRadiusY); |
| } |
| |
| /// Whether this rounded rectangle has no side with a straight section. |
| bool get isEllipse { |
| return tlRadius == trRadius && |
| trRadius == brRadius && |
| brRadius == blRadius && |
| width <= 2.0 * tlRadiusX && |
| height <= 2.0 * tlRadiusY; |
| } |
| |
| /// Whether this rounded rectangle would draw as a circle. |
| bool get isCircle => width == height && isEllipse; |
| |
| /// The lesser of the magnitudes of the [width] and the [height] of this |
| /// rounded rectangle. |
| double get shortestSide => math.min(width.abs(), height.abs()); |
| |
| /// The greater of the magnitudes of the [width] and the [height] of this |
| /// rounded rectangle. |
| double get longestSide => math.max(width.abs(), height.abs()); |
| |
| /// Whether any of the dimensions are `NaN`. |
| bool get hasNaN => |
| left.isNaN || |
| top.isNaN || |
| right.isNaN || |
| bottom.isNaN || |
| trRadiusX.isNaN || |
| trRadiusY.isNaN || |
| tlRadiusX.isNaN || |
| tlRadiusY.isNaN || |
| brRadiusX.isNaN || |
| brRadiusY.isNaN || |
| blRadiusX.isNaN || |
| blRadiusY.isNaN; |
| |
| /// The offset to the point halfway between the left and right and the top and |
| /// bottom edges of this rectangle. |
| Offset get center => Offset(left + width / 2.0, top + height / 2.0); |
| |
| // Returns the minimum between min and scale to which radius1 and radius2 |
| // should be scaled with in order not to exceed the limit. |
| double _getMin(double min, double radius1, double radius2, double limit) { |
| final double sum = radius1 + radius2; |
| if (sum > limit && sum != 0.0) { |
| return math.min(min, limit / sum); |
| } |
| return min; |
| } |
| |
| /// Scales all radii so that on each side their sum will not exceed the size |
| /// of the width/height. |
| /// |
| /// Skia already handles RRects with radii that are too large in this way. |
| /// Therefore, this method is only needed for use cases of [RRect] or |
| /// [RSuperellipse] that require the appropriately scaled radii values. |
| /// |
| /// See the [Skia scaling implementation](https://github.com/google/skia/blob/main/src/core/SkRRect.cpp) |
| /// for more details. |
| T scaleRadii() { |
| double scale = 1.0; |
| scale = _getMin(scale, blRadiusY, tlRadiusY, height); |
| scale = _getMin(scale, tlRadiusX, trRadiusX, width); |
| scale = _getMin(scale, trRadiusY, brRadiusY, height); |
| scale = _getMin(scale, brRadiusX, blRadiusX, width); |
| assert(scale >= 0); |
| |
| if (scale < 1.0) { |
| return _create( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: tlRadiusX * scale, |
| tlRadiusY: tlRadiusY * scale, |
| trRadiusX: trRadiusX * scale, |
| trRadiusY: trRadiusY * scale, |
| blRadiusX: blRadiusX * scale, |
| blRadiusY: blRadiusY * scale, |
| brRadiusX: brRadiusX * scale, |
| brRadiusY: brRadiusY * scale, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| return _create( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: tlRadiusX, |
| tlRadiusY: tlRadiusY, |
| trRadiusX: trRadiusX, |
| trRadiusY: trRadiusY, |
| blRadiusX: blRadiusX, |
| blRadiusY: blRadiusY, |
| brRadiusX: brRadiusX, |
| brRadiusY: brRadiusY, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| // Linearly interpolate between this object and another of the same shape. |
| T _lerpTo(T? b, double t) { |
| assert(runtimeType == T); |
| if (b == null) { |
| final double k = 1.0 - t; |
| return _create( |
| left: left * k, |
| top: top * k, |
| right: right * k, |
| bottom: bottom * k, |
| tlRadiusX: math.max(0, tlRadiusX * k), |
| tlRadiusY: math.max(0, tlRadiusY * k), |
| trRadiusX: math.max(0, trRadiusX * k), |
| trRadiusY: math.max(0, trRadiusY * k), |
| brRadiusX: math.max(0, brRadiusX * k), |
| brRadiusY: math.max(0, brRadiusY * k), |
| blRadiusX: math.max(0, blRadiusX * k), |
| blRadiusY: math.max(0, blRadiusY * k), |
| ); |
| } else { |
| return _create( |
| left: _lerpDouble(left, b.left, t), |
| top: _lerpDouble(top, b.top, t), |
| right: _lerpDouble(right, b.right, t), |
| bottom: _lerpDouble(bottom, b.bottom, t), |
| tlRadiusX: math.max(0, _lerpDouble(tlRadiusX, b.tlRadiusX, t)), |
| tlRadiusY: math.max(0, _lerpDouble(tlRadiusY, b.tlRadiusY, t)), |
| trRadiusX: math.max(0, _lerpDouble(trRadiusX, b.trRadiusX, t)), |
| trRadiusY: math.max(0, _lerpDouble(trRadiusY, b.trRadiusY, t)), |
| brRadiusX: math.max(0, _lerpDouble(brRadiusX, b.brRadiusX, t)), |
| brRadiusY: math.max(0, _lerpDouble(brRadiusY, b.brRadiusY, t)), |
| blRadiusX: math.max(0, _lerpDouble(blRadiusX, b.blRadiusX, t)), |
| blRadiusY: math.max(0, _lerpDouble(blRadiusY, b.blRadiusY, t)), |
| ); |
| } |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| bool operator ==(Object other) { |
| if (identical(this, other)) { |
| return true; |
| } |
| if (runtimeType != other.runtimeType) { |
| return false; |
| } |
| return other is _RRectLike && |
| other.left == left && |
| other.top == top && |
| other.right == right && |
| other.bottom == bottom && |
| other.tlRadiusX == tlRadiusX && |
| other.tlRadiusY == tlRadiusY && |
| other.trRadiusX == trRadiusX && |
| other.trRadiusY == trRadiusY && |
| other.blRadiusX == blRadiusX && |
| other.blRadiusY == blRadiusY && |
| other.brRadiusX == brRadiusX && |
| other.brRadiusY == brRadiusY; |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| int get hashCode => Object.hash( |
| left, |
| top, |
| right, |
| bottom, |
| tlRadiusX, |
| tlRadiusY, |
| trRadiusX, |
| trRadiusY, |
| blRadiusX, |
| blRadiusY, |
| brRadiusX, |
| brRadiusY, |
| ); |
| |
| String _toString({required String className}) { |
| final String rect = |
| '${left.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ' |
| '${top.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ' |
| '${right.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ' |
| '${bottom.toStringAsFixed(1)}'; |
| if (tlRadius == trRadius && trRadius == brRadius && brRadius == blRadius) { |
| if (tlRadius.x == tlRadius.y) { |
| return '$className.fromLTRBR($rect, ${tlRadius.x.toStringAsFixed(1)})'; |
| } |
| return '$className.fromLTRBXY($rect, ${tlRadius.x.toStringAsFixed(1)}, ${tlRadius.y.toStringAsFixed(1)})'; |
| } |
| return '$className.fromLTRBAndCorners(' |
| '$rect, ' |
| 'topLeft: $tlRadius, ' |
| 'topRight: $trRadius, ' |
| 'bottomRight: $brRadius, ' |
| 'bottomLeft: $blRadius' |
| ')'; |
| } |
| } |
| |
| /// An immutable rounded rectangle with the custom radii for all four corners. |
| class RRect extends _RRectLike<RRect> { |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its left, top, right, and bottom edges, |
| /// and the same radii along its horizontal axis and its vertical axis. |
| /// |
| /// Will assert in debug mode if `radiusX` or `radiusY` are negative. |
| const RRect.fromLTRBXY( |
| double left, |
| double top, |
| double right, |
| double bottom, |
| double radiusX, |
| double radiusY, |
| ) : this._raw( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: radiusX, |
| tlRadiusY: radiusY, |
| trRadiusX: radiusX, |
| trRadiusY: radiusY, |
| blRadiusX: radiusX, |
| blRadiusY: radiusY, |
| brRadiusX: radiusX, |
| brRadiusY: radiusY, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its left, top, right, and bottom edges, |
| /// and the same radius in each corner. |
| /// |
| /// Will assert in debug mode if the `radius` is negative in either x or y. |
| RRect.fromLTRBR(double left, double top, double right, double bottom, Radius radius) |
| : this._raw( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: radius.x, |
| tlRadiusY: radius.y, |
| trRadiusX: radius.x, |
| trRadiusY: radius.y, |
| blRadiusX: radius.x, |
| blRadiusY: radius.y, |
| brRadiusX: radius.x, |
| brRadiusY: radius.y, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its bounding box and the same radii |
| /// along its horizontal axis and its vertical axis. |
| /// |
| /// Will assert in debug mode if `radiusX` or `radiusY` are negative. |
| RRect.fromRectXY(Rect rect, double radiusX, double radiusY) |
| : this._raw( |
| top: rect.top, |
| left: rect.left, |
| right: rect.right, |
| bottom: rect.bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: radiusX, |
| tlRadiusY: radiusY, |
| trRadiusX: radiusX, |
| trRadiusY: radiusY, |
| blRadiusX: radiusX, |
| blRadiusY: radiusY, |
| brRadiusX: radiusX, |
| brRadiusY: radiusY, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its bounding box and a radius that is |
| /// the same in each corner. |
| /// |
| /// Will assert in debug mode if the `radius` is negative in either x or y. |
| RRect.fromRectAndRadius(Rect rect, Radius radius) |
| : this._raw( |
| top: rect.top, |
| left: rect.left, |
| right: rect.right, |
| bottom: rect.bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: radius.x, |
| tlRadiusY: radius.y, |
| trRadiusX: radius.x, |
| trRadiusY: radius.y, |
| blRadiusX: radius.x, |
| blRadiusY: radius.y, |
| brRadiusX: radius.x, |
| brRadiusY: radius.y, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its left, top, right, and bottom edges, |
| /// and topLeft, topRight, bottomRight, and bottomLeft radii. |
| /// |
| /// The corner radii default to [Radius.zero], i.e. right-angled corners. Will |
| /// assert in debug mode if any of the radii are negative in either x or y. |
| RRect.fromLTRBAndCorners( |
| double left, |
| double top, |
| double right, |
| double bottom, { |
| Radius topLeft = Radius.zero, |
| Radius topRight = Radius.zero, |
| Radius bottomRight = Radius.zero, |
| Radius bottomLeft = Radius.zero, |
| }) : this._raw( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: topLeft.x, |
| tlRadiusY: topLeft.y, |
| trRadiusX: topRight.x, |
| trRadiusY: topRight.y, |
| blRadiusX: bottomLeft.x, |
| blRadiusY: bottomLeft.y, |
| brRadiusX: bottomRight.x, |
| brRadiusY: bottomRight.y, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its bounding box and topLeft, |
| /// topRight, bottomRight, and bottomLeft radii. |
| /// |
| /// The corner radii default to [Radius.zero], i.e. right-angled corners. Will |
| /// assert in debug mode if any of the radii are negative in either x or y. |
| RRect.fromRectAndCorners( |
| Rect rect, { |
| Radius topLeft = Radius.zero, |
| Radius topRight = Radius.zero, |
| Radius bottomRight = Radius.zero, |
| Radius bottomLeft = Radius.zero, |
| }) : this._raw( |
| top: rect.top, |
| left: rect.left, |
| right: rect.right, |
| bottom: rect.bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: topLeft.x, |
| tlRadiusY: topLeft.y, |
| trRadiusX: topRight.x, |
| trRadiusY: topRight.y, |
| blRadiusX: bottomLeft.x, |
| blRadiusY: bottomLeft.y, |
| brRadiusX: bottomRight.x, |
| brRadiusY: bottomRight.y, |
| ); |
| |
| const RRect._raw({ |
| super.left = 0.0, |
| super.top = 0.0, |
| super.right = 0.0, |
| super.bottom = 0.0, |
| super.tlRadiusX = 0.0, |
| super.tlRadiusY = 0.0, |
| super.trRadiusX = 0.0, |
| super.trRadiusY = 0.0, |
| super.brRadiusX = 0.0, |
| super.brRadiusY = 0.0, |
| super.blRadiusX = 0.0, |
| super.blRadiusY = 0.0, |
| }); |
| |
| @override |
| RRect _create({ |
| required double left, |
| required double top, |
| required double right, |
| required double bottom, |
| required double tlRadiusX, |
| required double tlRadiusY, |
| required double trRadiusX, |
| required double trRadiusY, |
| required double brRadiusX, |
| required double brRadiusY, |
| required double blRadiusX, |
| required double blRadiusY, |
| }) => RRect._raw( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: tlRadiusX, |
| tlRadiusY: tlRadiusY, |
| trRadiusX: trRadiusX, |
| trRadiusY: trRadiusY, |
| blRadiusX: blRadiusX, |
| blRadiusY: blRadiusY, |
| brRadiusX: brRadiusX, |
| brRadiusY: brRadiusY, |
| ); |
| |
| Float32List _getValue32() { |
| final Float32List result = Float32List(12); |
| result[0] = left; |
| result[1] = top; |
| result[2] = right; |
| result[3] = bottom; |
| result[4] = tlRadiusX; |
| result[5] = tlRadiusY; |
| result[6] = trRadiusX; |
| result[7] = trRadiusY; |
| result[8] = brRadiusX; |
| result[9] = brRadiusY; |
| result[10] = blRadiusX; |
| result[11] = blRadiusY; |
| return result; |
| } |
| |
| /// A rounded rectangle with all the values set to zero. |
| static const RRect zero = RRect._raw(); |
| |
| /// Whether the point specified by the given offset (which is assumed to be |
| /// relative to the origin) lies inside the rounded rectangle. |
| /// |
| /// This method may allocate (and cache) a copy of the object with normalized |
| /// radii the first time it is called on a particular [RRect] instance. When |
| /// using this method, prefer to reuse existing [RRect]s rather than |
| /// recreating the object each time. |
| bool contains(Offset point) { |
| if (point.dx < left || point.dx >= right || point.dy < top || point.dy >= bottom) { |
| return false; |
| } // outside bounding box |
| |
| final RRect scaled = scaleRadii(); |
| |
| double x; |
| double y; |
| double radiusX; |
| double radiusY; |
| // check whether point is in one of the rounded corner areas |
| // x, y -> translate to ellipse center |
| if (point.dx < left + scaled.tlRadiusX && point.dy < top + scaled.tlRadiusY) { |
| x = point.dx - left - scaled.tlRadiusX; |
| y = point.dy - top - scaled.tlRadiusY; |
| radiusX = scaled.tlRadiusX; |
| radiusY = scaled.tlRadiusY; |
| } else if (point.dx > right - scaled.trRadiusX && point.dy < top + scaled.trRadiusY) { |
| x = point.dx - right + scaled.trRadiusX; |
| y = point.dy - top - scaled.trRadiusY; |
| radiusX = scaled.trRadiusX; |
| radiusY = scaled.trRadiusY; |
| } else if (point.dx > right - scaled.brRadiusX && point.dy > bottom - scaled.brRadiusY) { |
| x = point.dx - right + scaled.brRadiusX; |
| y = point.dy - bottom + scaled.brRadiusY; |
| radiusX = scaled.brRadiusX; |
| radiusY = scaled.brRadiusY; |
| } else if (point.dx < left + scaled.blRadiusX && point.dy > bottom - scaled.blRadiusY) { |
| x = point.dx - left - scaled.blRadiusX; |
| y = point.dy - bottom + scaled.blRadiusY; |
| radiusX = scaled.blRadiusX; |
| radiusY = scaled.blRadiusY; |
| } else { |
| return true; // inside and not within the rounded corner area |
| } |
| |
| x = x / radiusX; |
| y = y / radiusY; |
| // check if the point is outside the unit circle |
| if (x * x + y * y > 1.0) { |
| return false; |
| } |
| return true; |
| } |
| |
| /// Linearly interpolate between two rounded rectangles. |
| /// |
| /// If either is null, this function substitutes [RRect.zero] instead. |
| /// |
| /// The `t` argument represents position on the timeline, with 0.0 meaning |
| /// that the interpolation has not started, returning `a` (or something |
| /// equivalent to `a`), 1.0 meaning that the interpolation has finished, |
| /// returning `b` (or something equivalent to `b`), and values in between |
| /// meaning that the interpolation is at the relevant point on the timeline |
| /// between `a` and `b`. The interpolation can be extrapolated beyond 0.0 and |
| /// 1.0, so negative values and values greater than 1.0 are valid (and can |
| /// easily be generated by curves such as [Curves.elasticInOut]). |
| /// |
| /// Values for `t` are usually obtained from an [Animation<double>], such as |
| /// an [AnimationController]. |
| static RRect? lerp(RRect? a, RRect? b, double t) { |
| if (a == null) { |
| if (b == null) { |
| return null; |
| } |
| return b._lerpTo(null, 1 - t); |
| } |
| return a._lerpTo(b, t); |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| String toString() { |
| return _toString(className: 'RRect'); |
| } |
| } |
| |
| /// An immutable rounded superellipse. |
| /// |
| /// A rounded superellipse (not to be confused with a standard superellipse) is |
| /// a shape formed by replacing the four curved corners of a superellipse with |
| /// circular arcs. A (standard) superellipse follows the formula x^n + y^n = |
| /// a^n, and while n > 2 gives it rounded corners, they tend to be too sharp and |
| /// pronounced. Replacing them with circular arcs makes the shape feel softer |
| /// and more natural. |
| /// |
| /// Visually, a rounded superellipse looks similar to a typical rounded rectangle |
| /// ([RRect]) but with smoother transitions between the straight edges and |
| /// corners. It closely matches the `RoundedRectangle` shape in SwiftUI with the |
| /// `.continuous` corner style. |
| class RSuperellipse extends _RRectLike<RSuperellipse> { |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its left, top, right, and bottom edges, |
| /// and the same radii along its horizontal axis and its vertical axis. |
| /// |
| /// Will assert in debug mode if `radiusX` or `radiusY` are negative. |
| const RSuperellipse.fromLTRBXY( |
| double left, |
| double top, |
| double right, |
| double bottom, |
| double radiusX, |
| double radiusY, |
| ) : this._raw( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: radiusX, |
| tlRadiusY: radiusY, |
| trRadiusX: radiusX, |
| trRadiusY: radiusY, |
| blRadiusX: radiusX, |
| blRadiusY: radiusY, |
| brRadiusX: radiusX, |
| brRadiusY: radiusY, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its left, top, right, and bottom edges, |
| /// and the same radius in each corner. |
| /// |
| /// Will assert in debug mode if the `radius` is negative in either x or y. |
| RSuperellipse.fromLTRBR(double left, double top, double right, double bottom, Radius radius) |
| : this._raw( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: radius.x, |
| tlRadiusY: radius.y, |
| trRadiusX: radius.x, |
| trRadiusY: radius.y, |
| blRadiusX: radius.x, |
| blRadiusY: radius.y, |
| brRadiusX: radius.x, |
| brRadiusY: radius.y, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its bounding box and the same radii |
| /// along its horizontal axis and its vertical axis. |
| /// |
| /// Will assert in debug mode if `radiusX` or `radiusY` are negative. |
| RSuperellipse.fromRectXY(Rect rect, double radiusX, double radiusY) |
| : this._raw( |
| top: rect.top, |
| left: rect.left, |
| right: rect.right, |
| bottom: rect.bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: radiusX, |
| tlRadiusY: radiusY, |
| trRadiusX: radiusX, |
| trRadiusY: radiusY, |
| blRadiusX: radiusX, |
| blRadiusY: radiusY, |
| brRadiusX: radiusX, |
| brRadiusY: radiusY, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its bounding box and a radius that is |
| /// the same in each corner. |
| /// |
| /// Will assert in debug mode if the `radius` is negative in either x or y. |
| RSuperellipse.fromRectAndRadius(Rect rect, Radius radius) |
| : this._raw( |
| top: rect.top, |
| left: rect.left, |
| right: rect.right, |
| bottom: rect.bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: radius.x, |
| tlRadiusY: radius.y, |
| trRadiusX: radius.x, |
| trRadiusY: radius.y, |
| blRadiusX: radius.x, |
| blRadiusY: radius.y, |
| brRadiusX: radius.x, |
| brRadiusY: radius.y, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its left, top, right, and bottom edges, |
| /// and topLeft, topRight, bottomRight, and bottomLeft radii. |
| /// |
| /// The corner radii default to [Radius.zero], i.e. right-angled corners. Will |
| /// assert in debug mode if any of the radii are negative in either x or y. |
| RSuperellipse.fromLTRBAndCorners( |
| double left, |
| double top, |
| double right, |
| double bottom, { |
| Radius topLeft = Radius.zero, |
| Radius topRight = Radius.zero, |
| Radius bottomRight = Radius.zero, |
| Radius bottomLeft = Radius.zero, |
| }) : this._raw( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: topLeft.x, |
| tlRadiusY: topLeft.y, |
| trRadiusX: topRight.x, |
| trRadiusY: topRight.y, |
| blRadiusX: bottomLeft.x, |
| blRadiusY: bottomLeft.y, |
| brRadiusX: bottomRight.x, |
| brRadiusY: bottomRight.y, |
| ); |
| |
| /// Construct a rounded rectangle from its bounding box and topLeft, |
| /// topRight, bottomRight, and bottomLeft radii. |
| /// |
| /// The corner radii default to [Radius.zero], i.e. right-angled corners. Will |
| /// assert in debug mode if any of the radii are negative in either x or y. |
| RSuperellipse.fromRectAndCorners( |
| Rect rect, { |
| Radius topLeft = Radius.zero, |
| Radius topRight = Radius.zero, |
| Radius bottomRight = Radius.zero, |
| Radius bottomLeft = Radius.zero, |
| }) : this._raw( |
| top: rect.top, |
| left: rect.left, |
| right: rect.right, |
| bottom: rect.bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: topLeft.x, |
| tlRadiusY: topLeft.y, |
| trRadiusX: topRight.x, |
| trRadiusY: topRight.y, |
| blRadiusX: bottomLeft.x, |
| blRadiusY: bottomLeft.y, |
| brRadiusX: bottomRight.x, |
| brRadiusY: bottomRight.y, |
| ); |
| |
| const RSuperellipse._raw({ |
| super.left = 0.0, |
| super.top = 0.0, |
| super.right = 0.0, |
| super.bottom = 0.0, |
| super.tlRadiusX = 0.0, |
| super.tlRadiusY = 0.0, |
| super.trRadiusX = 0.0, |
| super.trRadiusY = 0.0, |
| super.brRadiusX = 0.0, |
| super.brRadiusY = 0.0, |
| super.blRadiusX = 0.0, |
| super.blRadiusY = 0.0, |
| }); |
| |
| @override |
| RSuperellipse _create({ |
| required double left, |
| required double top, |
| required double right, |
| required double bottom, |
| required double tlRadiusX, |
| required double tlRadiusY, |
| required double trRadiusX, |
| required double trRadiusY, |
| required double brRadiusX, |
| required double brRadiusY, |
| required double blRadiusX, |
| required double blRadiusY, |
| }) => RSuperellipse._raw( |
| top: top, |
| left: left, |
| right: right, |
| bottom: bottom, |
| tlRadiusX: tlRadiusX, |
| tlRadiusY: tlRadiusY, |
| trRadiusX: trRadiusX, |
| trRadiusY: trRadiusY, |
| blRadiusX: blRadiusX, |
| blRadiusY: blRadiusY, |
| brRadiusX: brRadiusX, |
| brRadiusY: brRadiusY, |
| ); |
| |
| _NativeRSuperellipse _native() { |
| return _NativeRSuperellipse(this); |
| } |
| |
| /// Whether the point specified by the given offset (which is assumed to be |
| /// relative to the origin) lies inside the rounded superellipse. |
| bool contains(Offset point) { |
| return _native().contains(point); |
| } |
| |
| /// A rounded rectangle with all the values set to zero. |
| static const RSuperellipse zero = RSuperellipse._raw(); |
| |
| /// Linearly interpolate between two rounded superellipses. |
| /// |
| /// If either is null, this function substitutes [RSuperellipse.zero] instead. |
| /// |
| /// The `t` argument represents position on the timeline, with 0.0 meaning |
| /// that the interpolation has not started, returning `a` (or something |
| /// equivalent to `a`), 1.0 meaning that the interpolation has finished, |
| /// returning `b` (or something equivalent to `b`), and values in between |
| /// meaning that the interpolation is at the relevant point on the timeline |
| /// between `a` and `b`. The interpolation can be extrapolated beyond 0.0 and |
| /// 1.0, so negative values and values greater than 1.0 are valid (and can |
| /// easily be generated by curves such as [Curves.elasticInOut]). |
| /// |
| /// Values for `t` are usually obtained from an [Animation<double>], such as |
| /// an [AnimationController]. |
| static RSuperellipse? lerp(RSuperellipse? a, RSuperellipse? b, double t) { |
| if (a == null) { |
| if (b == null) { |
| return null; |
| } |
| return b._lerpTo(null, 1 - t); |
| } |
| return a._lerpTo(b, t); |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| String toString() { |
| return _toString(className: 'RSuperellipse'); |
| } |
| } |
| |
| class _NativeRSuperellipse extends NativeFieldWrapperClass1 { |
| _NativeRSuperellipse(RSuperellipse rsuperellipse) { |
| _constructor( |
| rsuperellipse.left, |
| rsuperellipse.top, |
| rsuperellipse.right, |
| rsuperellipse.bottom, |
| rsuperellipse.tlRadiusX, |
| rsuperellipse.tlRadiusY, |
| rsuperellipse.trRadiusX, |
| rsuperellipse.trRadiusY, |
| rsuperellipse.brRadiusX, |
| rsuperellipse.brRadiusY, |
| rsuperellipse.blRadiusX, |
| rsuperellipse.blRadiusY, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| @Native< |
| Void Function( |
| Handle, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| Double, |
| ) |
| >(symbol: 'RSuperellipse::Create') |
| external void _constructor( |
| double left, |
| double top, |
| double right, |
| double bottom, |
| double tlRadiusX, |
| double tlRadiusY, |
| double trRadiusX, |
| double trRadiusY, |
| double brRadiusX, |
| double brRadiusY, |
| double blRadiusX, |
| double blRadiusY, |
| ); |
| |
| bool contains(Offset point) { |
| return _contains(point.dx, point.dy); |
| } |
| |
| @Native<Bool Function(Pointer<Void>, Double, Double)>( |
| symbol: 'RSuperellipse::contains', |
| isLeaf: true, |
| ) |
| external bool _contains(double x, double y); |
| } |
| |
| /// A transform consisting of a translation, a rotation, and a uniform scale. |
| /// |
| /// Used by [Canvas.drawAtlas]. This is a more efficient way to represent these |
| /// simple transformations than a full matrix. |
| // Modeled after Impeller's RSTransform. |
| class RSTransform { |
| /// Creates an RSTransform. |
| /// |
| /// An [RSTransform] expresses the combination of a translation, a rotation |
| /// around a particular point, and a scale factor. |
| /// |
| /// The first argument, `scos`, is the cosine of the rotation, multiplied by |
| /// the scale factor. |
| /// |
| /// The second argument, `ssin`, is the sine of the rotation, multiplied by |
| /// that same scale factor. |
| /// |
| /// The third argument is the x coordinate of the translation, minus the |
| /// `scos` argument multiplied by the x-coordinate of the rotation point, plus |
| /// the `ssin` argument multiplied by the y-coordinate of the rotation point. |
| /// |
| /// The fourth argument is the y coordinate of the translation, minus the `ssin` |
| /// argument multiplied by the x-coordinate of the rotation point, minus the |
| /// `scos` argument multiplied by the y-coordinate of the rotation point. |
| /// |
| /// The [RSTransform.fromComponents] method may be a simpler way to |
| /// construct these values. However, if there is a way to factor out the |
| /// computations of the sine and cosine of the rotation so that they can be |
| /// reused over multiple calls to this constructor, it may be more efficient |
| /// to directly use this constructor instead. |
| RSTransform(double scos, double ssin, double tx, double ty) { |
| _value |
| ..[0] = scos |
| ..[1] = ssin |
| ..[2] = tx |
| ..[3] = ty; |
| } |
| |
| /// Creates an RSTransform from its individual components. |
| /// |
| /// The `rotation` parameter gives the rotation in radians. |
| /// |
| /// The `scale` parameter describes the uniform scale factor. |
| /// |
| /// The `anchorX` and `anchorY` parameters give the coordinate of the point |
| /// around which to rotate. |
| /// |
| /// The `translateX` and `translateY` parameters give the coordinate of the |
| /// offset by which to translate. |
| /// |
| /// This constructor computes the arguments of the [RSTransform.new] |
| /// constructor and then defers to that constructor to actually create the |
| /// object. If many [RSTransform] objects are being created and there is a way |
| /// to factor out the computations of the sine and cosine of the rotation |
| /// (which are computed each time this constructor is called) and reuse them |
| /// over multiple [RSTransform] objects, it may be more efficient to directly |
| /// use the more direct [RSTransform.new] constructor instead. |
| factory RSTransform.fromComponents({ |
| required double rotation, |
| required double scale, |
| required double anchorX, |
| required double anchorY, |
| required double translateX, |
| required double translateY, |
| }) { |
| final double scos = math.cos(rotation) * scale; |
| final double ssin = math.sin(rotation) * scale; |
| final double tx = translateX + -scos * anchorX + ssin * anchorY; |
| final double ty = translateY + -ssin * anchorX - scos * anchorY; |
| return RSTransform(scos, ssin, tx, ty); |
| } |
| |
| final Float32List _value = Float32List(4); |
| |
| /// The cosine of the rotation multiplied by the scale factor. |
| double get scos => _value[0]; |
| |
| /// The sine of the rotation multiplied by that same scale factor. |
| double get ssin => _value[1]; |
| |
| /// The x coordinate of the translation, minus [scos] multiplied by the |
| /// x-coordinate of the rotation point, plus [ssin] multiplied by the |
| /// y-coordinate of the rotation point. |
| double get tx => _value[2]; |
| |
| /// The y coordinate of the translation, minus [ssin] multiplied by the |
| /// x-coordinate of the rotation point, minus [scos] multiplied by the |
| /// y-coordinate of the rotation point. |
| double get ty => _value[3]; |
| } |