| // Copyright 2014 The Flutter Authors. All rights reserved. |
| // Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be |
| // found in the LICENSE file. |
| |
| import 'dart:collection'; |
| import 'dart:ui' as ui show |
| ParagraphStyle, |
| StrutStyle, |
| TextStyle, |
| lerpDouble; |
| |
| import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart'; |
| |
| import 'basic_types.dart'; |
| import 'colors.dart'; |
| import 'strut_style.dart'; |
| import 'text_painter.dart'; |
| import 'text_scaler.dart'; |
| |
| const String _kDefaultDebugLabel = 'unknown'; |
| |
| const String _kColorForegroundWarning = 'Cannot provide both a color and a foreground\n' |
| 'The color argument is just a shorthand for "foreground: Paint()..color = color".'; |
| |
| const String _kColorBackgroundWarning = 'Cannot provide both a backgroundColor and a background\n' |
| 'The backgroundColor argument is just a shorthand for "background: Paint()..color = color".'; |
| |
| // Examples can assume: |
| // late BuildContext context; |
| |
| /// An immutable style describing how to format and paint text. |
| /// |
| /// {@youtube 560 315 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1z6YP7YmvwA} |
| /// |
| /// ### Bold |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// Here, a single line of text in a [Text] widget is given a specific style |
| /// override. The style is mixed with the ambient [DefaultTextStyle] by the |
| /// [Text] widget. |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const Text( |
| /// 'No, we need bold strokes. We need this plan.', |
| /// style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold), |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// ### Italics |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// As in the previous example, the [Text] widget is given a specific style |
| /// override which is implicitly mixed with the ambient [DefaultTextStyle]. |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const Text( |
| /// "Welcome to the present, we're running a real nation.", |
| /// style: TextStyle(fontStyle: FontStyle.italic), |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// ### Opacity and Color |
| /// |
| /// Each line here is progressively more opaque. The base color is |
| /// [material.Colors.black], and [Color.withOpacity] is used to create a |
| /// derivative color with the desired opacity. The root [TextSpan] for this |
| /// [RichText] widget is explicitly given the ambient [DefaultTextStyle], since |
| /// [RichText] does not do that automatically. The inner [TextStyle] objects are |
| /// implicitly mixed with the parent [TextSpan]'s [TextSpan.style]. |
| /// |
| /// If [color] is specified, [foreground] must be null and vice versa. [color] is |
| /// treated as a shorthand for `Paint()..color = color`. |
| /// |
| /// If [backgroundColor] is specified, [background] must be null and vice versa. |
| /// The [backgroundColor] is treated as a shorthand for |
| /// `background: Paint()..color = backgroundColor`. |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// RichText( |
| /// text: TextSpan( |
| /// style: DefaultTextStyle.of(context).style, |
| /// children: <TextSpan>[ |
| /// TextSpan( |
| /// text: "You don't have the votes.\n", |
| /// style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black.withOpacity(0.6)), |
| /// ), |
| /// TextSpan( |
| /// text: "You don't have the votes!\n", |
| /// style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black.withOpacity(0.8)), |
| /// ), |
| /// TextSpan( |
| /// text: "You're gonna need congressional approval and you don't have the votes!\n", |
| /// style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black.withOpacity(1.0)), |
| /// ), |
| /// ], |
| /// ), |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// |
| /// ### Size |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// In this example, the ambient [DefaultTextStyle] is explicitly manipulated to |
| /// obtain a [TextStyle] that doubles the default font size. |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// Text( |
| /// "These are wise words, enterprising men quote 'em.", |
| /// style: DefaultTextStyle.of(context).style.apply(fontSizeFactor: 2.0), |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// ### Line height |
| /// |
| /// By default, text will layout with line height as defined by the font. |
| /// Font-metrics defined line height may be taller or shorter than the font size. |
| /// The [height] property allows manual adjustment of the height of the line as |
| /// a multiple of [fontSize]. For most fonts, setting [height] to 1.0 is not |
| /// the same as omitting or setting height to null. The following diagram |
| /// illustrates the difference between the font-metrics-defined line height and |
| /// the line height produced with `height: 1.0` (also known as the EM-square): |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// The [height] property can be used to change the line height. Here, the line |
| /// height is set to 5 times the font size, so that the text is very spaced out. |
| /// Since the `fontSize` is set to 10, the final height of the line is |
| /// 50 pixels. |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const Text( |
| /// 'Ladies and gentlemen, you coulda been anywhere in the world tonight, but you’re here with us in New York City.', |
| /// style: TextStyle(height: 5, fontSize: 10), |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// Examples of the resulting heights from different values of `TextStyle.height`: |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// See [StrutStyle] for further control of line height at the paragraph level. |
| /// |
| /// ### Leading Distribution and Trimming |
| /// |
| /// [Leading](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leading) is the vertical space |
| /// between glyphs from adjacent lines. Quantitatively, it is the line height |
| /// (see the previous section) subtracted by the font's ascent and descent. |
| /// It's possible to have a negative `Leading` if [height] is sufficiently |
| /// small. |
| /// |
| /// When the [height] multiplier is null, `leading` and how it is distributed |
| /// is up to the font's |
| /// [metrics](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Typeface#Font_metrics). |
| /// When the [height] multiplier is specified, the exact behavior can be |
| /// configured via [leadingDistribution] and [TextPainter.textHeightBehavior]. |
| /// |
| /// 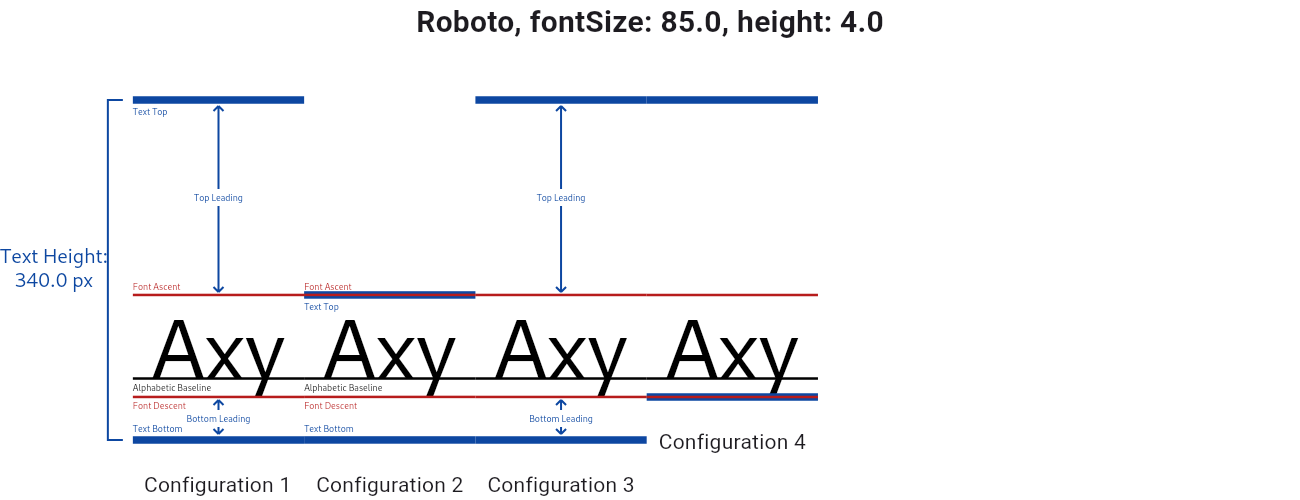 |
| /// |
| /// Above is a side-by-side comparison of different [leadingDistribution] and |
| /// [TextPainter.textHeightBehavior] combinations. |
| /// |
| /// * Configuration 1: The default. [leadingDistribution] is set to [TextLeadingDistribution.proportional]. |
| /// * Configuration 2: same as Configuration 1, except [TextHeightBehavior.applyHeightToFirstAscent] is set to false. |
| /// * Configuration 3: [leadingDistribution] is set to [TextLeadingDistribution.even]. |
| /// * Configuration 4: same as Configuration 3, except [TextHeightBehavior.applyHeightToLastDescent] is set to false. |
| /// |
| /// The [leadingDistribution] property controls how leading is distributed over |
| /// and under the text. With [TextLeadingDistribution.proportional] |
| /// (Configuration 1), `Top Leading : Bottom Leading = Font Ascent : Font |
| /// Descent`, which also means the alphabetic baseline divides the line height |
| /// into 2 parts proportional to the font's ascent and descent. With |
| /// [TextLeadingDistribution.even] (Configuration 3), `Top Leading` equals |
| /// `Bottom Leading`, and the glyphs are roughly centered within the allotted |
| /// line height. |
| /// |
| /// The [TextPainter.textHeightBehavior] is a property that controls leading at |
| /// the paragraph level. The `applyHeightToFirstAscent` property is applied |
| /// **after** [height] and [leadingDistribution]. Setting it to false trims the |
| /// "Top Leading" of the text box to match the font's ascent if it's on the |
| /// first line (see Configuration 2). Similarly setting |
| /// `applyHeightToLastDescent` to false reduces "Bottom Leading" to 0 for the |
| /// last line of text (Configuration 4). |
| /// |
| /// ### Wavy red underline with black text |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// Styles can be combined. In this example, the misspelled word is drawn in |
| /// black text and underlined with a wavy red line to indicate a spelling error. |
| /// (The remainder is styled according to the Flutter default text styles, not |
| /// the ambient [DefaultTextStyle], since no explicit style is given and |
| /// [RichText] does not automatically use the ambient [DefaultTextStyle].) |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// RichText( |
| /// text: const TextSpan( |
| /// text: "Don't tax the South ", |
| /// children: <TextSpan>[ |
| /// TextSpan( |
| /// text: 'cuz', |
| /// style: TextStyle( |
| /// color: Colors.black, |
| /// decoration: TextDecoration.underline, |
| /// decorationColor: Colors.red, |
| /// decorationStyle: TextDecorationStyle.wavy, |
| /// ), |
| /// ), |
| /// TextSpan( |
| /// text: ' we got it made in the shade', |
| /// ), |
| /// ], |
| /// ), |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// ### Borders and stroke (Foreground) |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// To create bordered text, a [Paint] with [Paint.style] set to [PaintingStyle.stroke] |
| /// should be provided as a [foreground] paint. The following example uses a [Stack] |
| /// to produce a stroke and fill effect. |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// Stack( |
| /// children: <Widget>[ |
| /// // Stroked text as border. |
| /// Text( |
| /// 'Greetings, planet!', |
| /// style: TextStyle( |
| /// fontSize: 40, |
| /// foreground: Paint() |
| /// ..style = PaintingStyle.stroke |
| /// ..strokeWidth = 6 |
| /// ..color = Colors.blue[700]!, |
| /// ), |
| /// ), |
| /// // Solid text as fill. |
| /// Text( |
| /// 'Greetings, planet!', |
| /// style: TextStyle( |
| /// fontSize: 40, |
| /// color: Colors.grey[300], |
| /// ), |
| /// ), |
| /// ], |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// ### Gradients (Foreground) |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// The [foreground] property also allows effects such as gradients to be |
| /// applied to the text. Here we provide a [Paint] with a [ui.Gradient] |
| /// shader. |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// Text( |
| /// 'Greetings, planet!', |
| /// style: TextStyle( |
| /// fontSize: 40, |
| /// foreground: Paint() |
| /// ..shader = ui.Gradient.linear( |
| /// const Offset(0, 20), |
| /// const Offset(150, 20), |
| /// <Color>[ |
| /// Colors.red, |
| /// Colors.yellow, |
| /// ], |
| /// ) |
| /// ), |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// ### Custom Fonts |
| /// |
| /// Custom fonts can be declared in the `pubspec.yaml` file as shown below: |
| /// |
| /// ```yaml |
| /// flutter: |
| /// fonts: |
| /// - family: Raleway |
| /// fonts: |
| /// - asset: fonts/Raleway-Regular.ttf |
| /// - asset: fonts/Raleway-Medium.ttf |
| /// weight: 500 |
| /// - asset: assets/fonts/Raleway-SemiBold.ttf |
| /// weight: 600 |
| /// - family: Schyler |
| /// fonts: |
| /// - asset: fonts/Schyler-Regular.ttf |
| /// - asset: fonts/Schyler-Italic.ttf |
| /// style: italic |
| /// ``` |
| /// |
| /// The `family` property determines the name of the font, which you can use in |
| /// the [fontFamily] argument. The `asset` property is a path to the font file, |
| /// relative to the `pubspec.yaml` file. The `weight` property specifies the |
| /// weight of the glyph outlines in the file as an integer multiple of 100 |
| /// between 100 and 900. This corresponds to the [FontWeight] class and can be |
| /// used in the [fontWeight] argument. The `style` property specifies whether the |
| /// outlines in the file are `italic` or `normal`. These values correspond to |
| /// the [FontStyle] class and can be used in the [fontStyle] argument. |
| /// |
| /// To select a custom font, create [TextStyle] using the [fontFamily] |
| /// argument as shown in the example below: |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const TextStyle(fontFamily: 'Raleway') |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// To use a font family defined in a package, the `package` argument must be |
| /// provided. For instance, suppose the font declaration above is in the |
| /// `pubspec.yaml` of a package named `my_package` which the app depends on. |
| /// Then creating the TextStyle is done as follows: |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const TextStyle(fontFamily: 'Raleway', package: 'my_package') |
| /// ``` |
| /// |
| /// If the package internally uses the font it defines, it should still specify |
| /// the `package` argument when creating the text style as in the example above. |
| /// |
| /// A package can also provide font files without declaring a font in its |
| /// `pubspec.yaml`. These files should then be in the `lib/` folder of the |
| /// package. The font files will not automatically be bundled in the app, instead |
| /// the app can use these selectively when declaring a font. Suppose a package |
| /// named `my_package` has: |
| /// |
| /// lib/fonts/Raleway-Medium.ttf |
| /// |
| /// Then the app can declare a font like in the example below: |
| /// |
| /// ```yaml |
| /// flutter: |
| /// fonts: |
| /// - family: Raleway |
| /// fonts: |
| /// - asset: assets/fonts/Raleway-Regular.ttf |
| /// - asset: packages/my_package/fonts/Raleway-Medium.ttf |
| /// weight: 500 |
| /// ``` |
| /// |
| /// The `lib/` is implied, so it should not be included in the asset path. |
| /// |
| /// In this case, since the app locally defines the font, the TextStyle is |
| /// created without the `package` argument: |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const TextStyle(fontFamily: 'Raleway') |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// #### Supported font formats |
| /// |
| /// Font formats currently supported by Flutter: |
| /// |
| /// * `.ttc` |
| /// * `.ttf` |
| /// * `.otf` |
| /// |
| /// Flutter does not support `.woff` and `.woff2` fonts for all platforms. |
| /// |
| /// ### Custom Font Fallback |
| /// |
| /// A custom [fontFamilyFallback] list can be provided. The list should be an |
| /// ordered list of strings of font family names in the order they will be attempted. |
| /// |
| /// The fonts in [fontFamilyFallback] will be used only if the requested glyph is |
| /// not present in the [fontFamily]. |
| /// |
| /// The fallback order is: |
| /// |
| /// * [fontFamily] |
| /// * [fontFamilyFallback] in order of first to last. |
| /// * System fallback fonts which will vary depending on platform. |
| /// |
| /// The glyph used will always be the first matching version in fallback order. |
| /// |
| /// The [fontFamilyFallback] property is commonly used to specify different font |
| /// families for multilingual text spans as well as separate fonts for glyphs such |
| /// as emojis. |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// In the following example, any glyphs not present in the font `Raleway` will be attempted |
| /// to be resolved with `Noto Sans CJK SC`, and then with `Noto Color Emoji`: |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const TextStyle( |
| /// fontFamily: 'Raleway', |
| /// fontFamilyFallback: <String>[ |
| /// 'Noto Sans CJK SC', |
| /// 'Noto Color Emoji', |
| /// ], |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// If all custom fallback font families are exhausted and no match was found |
| /// or no custom fallback was provided, the platform font fallback will be used. |
| /// |
| /// ### Inconsistent platform fonts |
| /// |
| /// By default, fonts differ depending on the platform. |
| /// |
| /// * The default font-family for `Android`,`Fuchsia` and `Linux` is `Roboto`. |
| /// * The default font-family for `iOS` is `SF Pro Display`/`SF Pro Text`. |
| /// * The default font-family for `MacOS` is `.AppleSystemUIFont`. |
| /// * The default font-family for `Windows` is `Segoe UI`. |
| // |
| // The implementation of these defaults can be found in: |
| // /packages/flutter/lib/src/material/typography.dart |
| /// |
| /// Since Flutter's font discovery for default fonts depends on the fonts present |
| /// on the device, it is not safe to assume all default fonts will be available or |
| /// consistent across devices. |
| /// |
| /// A known example of this is that Samsung devices ship with a CJK font that has |
| /// smaller line spacing than the Android default. This results in Samsung devices |
| /// displaying more tightly spaced text than on other Android devices when no |
| /// custom font is specified. |
| /// |
| /// To avoid this, a custom font should be specified if absolute font consistency |
| /// is required for your application. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [Text], the widget for showing text in a single style. |
| /// * [DefaultTextStyle], the widget that specifies the default text styles for |
| /// [Text] widgets, configured using a [TextStyle]. |
| /// * [RichText], the widget for showing a paragraph of mix-style text. |
| /// * [TextSpan], the class that wraps a [TextStyle] for the purposes of |
| /// passing it to a [RichText]. |
| /// * [TextStyle](https://api.flutter.dev/flutter/dart-ui/TextStyle-class.html), the class in the [dart:ui] library. |
| /// * Cookbook: [Use a custom font](https://flutter.dev/docs/cookbook/design/fonts) |
| /// * Cookbook: [Use themes to share colors and font styles](https://flutter.dev/docs/cookbook/design/themes) |
| @immutable |
| class TextStyle with Diagnosticable { |
| /// Creates a text style. |
| /// |
| /// The `package` argument must be non-null if the font family is defined in a |
| /// package. It is combined with the `fontFamily` argument to set the |
| /// [fontFamily] property. |
| /// |
| /// On Apple devices the strings 'CupertinoSystemText' and |
| /// 'CupertinoSystemDisplay' are used in [fontFamily] as proxies for the |
| /// Apple system fonts. They currently redirect to the equivilant of SF Pro |
| /// Text and SF Pro Display respectively. 'CupertinoSystemText' is designed |
| /// for fonts below 20 point size, and 'CupertinoSystemDisplay' is recommended |
| /// for sizes 20 and above. When used on non-Apple platforms, these strings |
| /// will return the regular fallback font family instead. |
| const TextStyle({ |
| this.inherit = true, |
| this.color, |
| this.backgroundColor, |
| this.fontSize, |
| this.fontWeight, |
| this.fontStyle, |
| this.letterSpacing, |
| this.wordSpacing, |
| this.textBaseline, |
| this.height, |
| this.leadingDistribution, |
| this.locale, |
| this.foreground, |
| this.background, |
| this.shadows, |
| this.fontFeatures, |
| this.fontVariations, |
| this.decoration, |
| this.decorationColor, |
| this.decorationStyle, |
| this.decorationThickness, |
| this.debugLabel, |
| String? fontFamily, |
| List<String>? fontFamilyFallback, |
| String? package, |
| this.overflow, |
| }) : fontFamily = package == null ? fontFamily : 'packages/$package/$fontFamily', |
| _fontFamilyFallback = fontFamilyFallback, |
| _package = package, |
| assert(color == null || foreground == null, _kColorForegroundWarning), |
| assert(backgroundColor == null || background == null, _kColorBackgroundWarning); |
| |
| |
| /// Whether null values in this [TextStyle] can be replaced with their value |
| /// in another [TextStyle] using [merge]. |
| /// |
| /// The [merge] operation is not commutative: the [inherit] value of the |
| /// method argument decides whether the two [TextStyle]s can be combined |
| /// together. If it is false, the method argument [TextStyle] will be returned. |
| /// Otherwise, the combining is allowed, and the returned [TextStyle] inherits |
| /// the [inherit] value from the method receiver. |
| /// |
| /// This property does not affect the text style inheritance in an [InlineSpan] |
| /// tree: an [InlineSpan]'s text style is merged with that of an ancestor |
| /// [InlineSpan] if it has unspecified fields, regardless of its [inherit] |
| /// value. |
| /// |
| /// Properties that don't have explicit values or other default values to fall |
| /// back to will revert to the defaults: white in color, a font size of 14 |
| /// pixels, in a sans-serif font face. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// * [TextStyle.merge], which can be used to combine properties from two |
| /// [TextStyle]s. |
| final bool inherit; |
| |
| /// The color to use when painting the text. |
| /// |
| /// If [foreground] is specified, this value must be null. The [color] property |
| /// is shorthand for `Paint()..color = color`. |
| /// |
| /// In [merge], [apply], and [lerp], conflicts between [color] and [foreground] |
| /// specification are resolved in [foreground]'s favor - i.e. if [foreground] is |
| /// specified in one place, it will dominate [color] in another. |
| final Color? color; |
| |
| /// The color to use as the background for the text. |
| /// |
| /// If [background] is specified, this value must be null. The |
| /// [backgroundColor] property is shorthand for |
| /// `background: Paint()..color = backgroundColor`. |
| /// |
| /// In [merge], [apply], and [lerp], conflicts between [backgroundColor] and [background] |
| /// specification are resolved in [background]'s favor - i.e. if [background] is |
| /// specified in one place, it will dominate [color] in another. |
| final Color? backgroundColor; |
| |
| /// The name of the font to use when painting the text (e.g., Roboto). |
| /// |
| /// If the font is defined in a package, this will be prefixed with |
| /// 'packages/package_name/' (e.g. 'packages/cool_fonts/Roboto'). The |
| /// prefixing is done by the constructor when the `package` argument is |
| /// provided. |
| /// |
| /// The value provided in [fontFamily] will act as the preferred/first font |
| /// family that glyphs are looked for in, followed in order by the font families |
| /// in [fontFamilyFallback]. When [fontFamily] is null or not provided, the |
| /// first value in [fontFamilyFallback] acts as the preferred/first font |
| /// family. When neither is provided, then the default platform font will |
| /// be used. |
| /// |
| /// When running on Apple devices, the strings 'CupertinoSystemText' and |
| /// 'CupertinoSystemDisplay' are used as proxies for the Apple system fonts. |
| /// They currently redirect to the equivilant of SF Pro Text and SF Pro Display |
| /// respectively. 'CupertinoSystemText' is designed for fonts below 20 point |
| /// size, and 'CupertinoSystemDisplay' is recommended for sizes 20 and above. |
| /// When used on non-Apple platforms, these strings will return the regular |
| /// fallback font family instead. |
| final String? fontFamily; |
| |
| /// The ordered list of font families to fall back on when a glyph cannot be |
| /// found in a higher priority font family. |
| /// |
| /// The value provided in [fontFamily] will act as the preferred/first font |
| /// family that glyphs are looked for in, followed in order by the font families |
| /// in [fontFamilyFallback]. If all font families are exhausted and no match |
| /// was found, the default platform font family will be used instead. |
| /// |
| /// When [fontFamily] is null or not provided, the first value in [fontFamilyFallback] |
| /// acts as the preferred/first font family. When neither is provided, then |
| /// the default platform font will be used. Providing an empty list or null |
| /// for this property is the same as omitting it. |
| /// |
| /// For example, if a glyph is not found in [fontFamily], then each font family |
| /// in [fontFamilyFallback] will be searched in order until it is found. If it |
| /// is not found, then a box will be drawn in its place. |
| /// |
| /// If the font is defined in a package, each font family in the list will be |
| /// prefixed with 'packages/package_name/' (e.g. 'packages/cool_fonts/Roboto'). |
| /// The package name should be provided by the `package` argument in the |
| /// constructor. |
| List<String>? get fontFamilyFallback => _package == null ? _fontFamilyFallback : _fontFamilyFallback?.map((String str) => 'packages/$_package/$str').toList(); |
| final List<String>? _fontFamilyFallback; |
| |
| // This is stored in order to prefix the fontFamilies in _fontFamilyFallback |
| // in the [fontFamilyFallback] getter. |
| final String? _package; |
| |
| /// The size of fonts (in logical pixels) to use when painting the text. |
| /// |
| /// The value specified matches the dimension of the |
| /// [em square](https://fonts.google.com/knowledge/glossary/em) of the |
| /// underlying font, and more often then not isn't exactly the height or the |
| /// width of glyphs in the font. |
| /// |
| /// During painting, the [fontSize] is multiplied by the current |
| /// `textScaleFactor` to let users make it easier to read text by increasing |
| /// its size. |
| /// |
| /// The [getParagraphStyle] method defaults to 14 logical pixels if [fontSize] |
| /// is set to null. |
| final double? fontSize; |
| |
| /// The typeface thickness to use when painting the text (e.g., bold). |
| final FontWeight? fontWeight; |
| |
| /// The typeface variant to use when drawing the letters (e.g., italics). |
| final FontStyle? fontStyle; |
| |
| /// The amount of space (in logical pixels) to add between each letter. |
| /// A negative value can be used to bring the letters closer. |
| final double? letterSpacing; |
| |
| /// The amount of space (in logical pixels) to add at each sequence of |
| /// white-space (i.e. between each word). A negative value can be used to |
| /// bring the words closer. |
| final double? wordSpacing; |
| |
| /// The common baseline that should be aligned between this text span and its |
| /// parent text span, or, for the root text spans, with the line box. |
| final TextBaseline? textBaseline; |
| |
| /// The height of this text span, as a multiple of the font size. |
| /// |
| /// When [height] is null or omitted, the line height will be determined |
| /// by the font's metrics directly, which may differ from the fontSize. |
| /// When [height] is non-null, the line height of the span of text will be a |
| /// multiple of [fontSize] and be exactly `fontSize * height` logical pixels |
| /// tall. |
| /// |
| /// For most fonts, setting [height] to 1.0 is not the same as omitting or |
| /// setting height to null because the [fontSize] sets the height of the EM-square, |
| /// which is different than the font provided metrics for line height. The |
| /// following diagram illustrates the difference between the font-metrics |
| /// defined line height and the line height produced with `height: 1.0` |
| /// (which forms the upper and lower edges of the EM-square): |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// Examples of the resulting line heights from different values of `TextStyle.height`: |
| /// |
| ///  |
| /// |
| /// See [StrutStyle] and [TextHeightBehavior] for further control of line |
| /// height at the paragraph level. |
| final double? height; |
| |
| /// How the vertical space added by the [height] multiplier should be |
| /// distributed over and under the text. |
| /// |
| /// When a non-null [height] is specified, after accommodating the glyphs of |
| /// the text, the remaining vertical space from the allotted line height will |
| /// be distributed over and under the text, according to the |
| /// [leadingDistribution] property. See the [TextStyle] class's documentation |
| /// for an example. |
| /// |
| /// When [height] is null, [leadingDistribution] does not affect the text |
| /// layout. |
| /// |
| /// Defaults to null, which defers to the paragraph's |
| /// `ParagraphStyle.textHeightBehavior`'s [leadingDistribution]. |
| final TextLeadingDistribution? leadingDistribution; |
| |
| /// The locale used to select region-specific glyphs. |
| /// |
| /// This property is rarely set. Typically the locale used to select |
| /// region-specific glyphs is defined by the text widget's [BuildContext] |
| /// using `Localizations.localeOf(context)`. For example [RichText] defines |
| /// its locale this way. However, a rich text widget's [TextSpan]s could |
| /// specify text styles with different explicit locales in order to select |
| /// different region-specific glyphs for each text span. |
| final Locale? locale; |
| |
| /// The paint drawn as a foreground for the text. |
| /// |
| /// The value should ideally be cached and reused each time if multiple text |
| /// styles are created with the same paint settings. Otherwise, each time it |
| /// will appear like the style changed, which will result in unnecessary |
| /// updates all the way through the framework. |
| /// |
| /// If [color] is specified, this value must be null. The [color] property |
| /// is shorthand for `Paint()..color = color`. |
| /// |
| /// In [merge], [apply], and [lerp], conflicts between [color] and [foreground] |
| /// specification are resolved in [foreground]'s favor - i.e. if [foreground] is |
| /// specified in one place, it will dominate [color] in another. |
| final Paint? foreground; |
| |
| /// The paint drawn as a background for the text. |
| /// |
| /// The value should ideally be cached and reused each time if multiple text |
| /// styles are created with the same paint settings. Otherwise, each time it |
| /// will appear like the style changed, which will result in unnecessary |
| /// updates all the way through the framework. |
| /// |
| /// If [backgroundColor] is specified, this value must be null. The |
| /// [backgroundColor] property is shorthand for |
| /// `background: Paint()..color = backgroundColor`. |
| /// |
| /// In [merge], [apply], and [lerp], conflicts between [backgroundColor] and |
| /// [background] specification are resolved in [background]'s favor - i.e. if |
| /// [background] is specified in one place, it will dominate [backgroundColor] |
| /// in another. |
| final Paint? background; |
| |
| /// The decorations to paint near the text (e.g., an underline). |
| /// |
| /// Multiple decorations can be applied using [TextDecoration.combine]. |
| final TextDecoration? decoration; |
| |
| /// The color in which to paint the text decorations. |
| final Color? decorationColor; |
| |
| /// The style in which to paint the text decorations (e.g., dashed). |
| final TextDecorationStyle? decorationStyle; |
| |
| /// The thickness of the decoration stroke as a multiplier of the thickness |
| /// defined by the font. |
| /// |
| /// The font provides a base stroke width for [decoration]s which scales off |
| /// of the [fontSize]. This property may be used to achieve a thinner or |
| /// thicker decoration stroke, without changing the [fontSize]. For example, |
| /// a [decorationThickness] of 2.0 will draw a decoration twice as thick as |
| /// the font defined decoration thickness. |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// To achieve a bolded strike-through, we can apply a thicker stroke for the |
| /// decoration. |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const Text( |
| /// 'This has a very BOLD strike through!', |
| /// style: TextStyle( |
| /// decoration: TextDecoration.lineThrough, |
| /// decorationThickness: 2.85, |
| /// ), |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// {@tool snippet} |
| /// We can apply a very thin and subtle wavy underline (perhaps, when words |
| /// are misspelled) by using a [decorationThickness] < 1.0. |
| /// |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const Text( |
| /// 'oopsIforgottousespaces!', |
| /// style: TextStyle( |
| /// decoration: TextDecoration.underline, |
| /// decorationStyle: TextDecorationStyle.wavy, |
| /// decorationColor: Colors.red, |
| /// decorationThickness: 0.5, |
| /// ), |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// {@end-tool} |
| /// |
| /// The default [decorationThickness] is 1.0, which will use the font's base |
| /// stroke thickness/width. |
| final double? decorationThickness; |
| |
| /// A human-readable description of this text style. |
| /// |
| /// This property is maintained only in debug builds. |
| /// |
| /// When merging ([merge]), copying ([copyWith]), modifying using [apply], or |
| /// interpolating ([lerp]), the label of the resulting style is marked with |
| /// the debug labels of the original styles. This helps figuring out where a |
| /// particular text style came from. |
| /// |
| /// This property is not considered when comparing text styles using `==` or |
| /// [compareTo], and it does not affect [hashCode]. |
| final String? debugLabel; |
| |
| /// A list of [Shadow]s that will be painted underneath the text. |
| /// |
| /// Multiple shadows are supported to replicate lighting from multiple light |
| /// sources. |
| /// |
| /// Shadows must be in the same order for [TextStyle] to be considered as |
| /// equivalent as order produces differing transparency. |
| final List<Shadow>? shadows; |
| |
| /// A list of [FontFeature]s that affect how the font selects glyphs. |
| /// |
| /// Some fonts support multiple variants of how a given character can be |
| /// rendered. For example, a font might provide both proportional and |
| /// tabular numbers, or it might offer versions of the zero digit with |
| /// and without slashes. [FontFeature]s can be used to select which of |
| /// these variants will be used for rendering. |
| /// |
| /// Font features are not interpolated by [lerp]. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [fontVariations], for font features that have continuous parameters. |
| final List<FontFeature>? fontFeatures; |
| |
| /// A list of [FontVariation]s that affect how a variable font is rendered. |
| /// |
| /// Some fonts are variable fonts that can generate multiple font faces based |
| /// on the values of customizable attributes. For example, a variable font |
| /// may have a weight axis that can be set to a value between 1 and 1000. |
| /// [FontVariation]s can be used to select the values of these design axes. |
| /// |
| /// For example, to control the weight axis of the Roboto Slab variable font |
| /// (https://fonts.google.com/specimen/Roboto+Slab): |
| /// ```dart |
| /// const TextStyle( |
| /// fontFamily: 'RobotoSlab', |
| /// fontVariations: <FontVariation>[FontVariation('wght', 900.0)] |
| /// ) |
| /// ``` |
| /// |
| /// Font variations can be interpolated via [lerp]. This is fastest when the |
| /// same font variation axes are specified, in the same order, in both |
| /// [TextStyle] objects. See [lerpFontVariations]. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [fontFeatures], for font variations that have discrete values. |
| final List<FontVariation>? fontVariations; |
| |
| /// How visual text overflow should be handled. |
| final TextOverflow? overflow; |
| |
| // Return the original value of fontFamily, without the additional |
| // "packages/$_package/" prefix. |
| String? get _fontFamily { |
| if (_package != null) { |
| final String fontFamilyPrefix = 'packages/$_package/'; |
| assert(fontFamily?.startsWith(fontFamilyPrefix) ?? true); |
| return fontFamily?.substring(fontFamilyPrefix.length); |
| } |
| return fontFamily; |
| } |
| |
| /// Creates a copy of this text style but with the given fields replaced with |
| /// the new values. |
| /// |
| /// One of [color] or [foreground] must be null, and if this has [foreground] |
| /// specified it will be given preference over any color parameter. |
| /// |
| /// One of [backgroundColor] or [background] must be null, and if this has |
| /// [background] specified it will be given preference over any |
| /// backgroundColor parameter. |
| TextStyle copyWith({ |
| bool? inherit, |
| Color? color, |
| Color? backgroundColor, |
| double? fontSize, |
| FontWeight? fontWeight, |
| FontStyle? fontStyle, |
| double? letterSpacing, |
| double? wordSpacing, |
| TextBaseline? textBaseline, |
| double? height, |
| TextLeadingDistribution? leadingDistribution, |
| Locale? locale, |
| Paint? foreground, |
| Paint? background, |
| List<Shadow>? shadows, |
| List<FontFeature>? fontFeatures, |
| List<FontVariation>? fontVariations, |
| TextDecoration? decoration, |
| Color? decorationColor, |
| TextDecorationStyle? decorationStyle, |
| double? decorationThickness, |
| String? debugLabel, |
| String? fontFamily, |
| List<String>? fontFamilyFallback, |
| String? package, |
| TextOverflow? overflow, |
| }) { |
| assert(color == null || foreground == null, _kColorForegroundWarning); |
| assert(backgroundColor == null || background == null, _kColorBackgroundWarning); |
| String? newDebugLabel; |
| assert(() { |
| if (this.debugLabel != null) { |
| newDebugLabel = debugLabel ?? '(${this.debugLabel}).copyWith'; |
| } |
| return true; |
| }()); |
| |
| return TextStyle( |
| inherit: inherit ?? this.inherit, |
| color: this.foreground == null && foreground == null ? color ?? this.color : null, |
| backgroundColor: this.background == null && background == null ? backgroundColor ?? this.backgroundColor : null, |
| fontSize: fontSize ?? this.fontSize, |
| fontWeight: fontWeight ?? this.fontWeight, |
| fontStyle: fontStyle ?? this.fontStyle, |
| letterSpacing: letterSpacing ?? this.letterSpacing, |
| wordSpacing: wordSpacing ?? this.wordSpacing, |
| textBaseline: textBaseline ?? this.textBaseline, |
| height: height ?? this.height, |
| leadingDistribution: leadingDistribution ?? this.leadingDistribution, |
| locale: locale ?? this.locale, |
| foreground: foreground ?? this.foreground, |
| background: background ?? this.background, |
| shadows: shadows ?? this.shadows, |
| fontFeatures: fontFeatures ?? this.fontFeatures, |
| fontVariations: fontVariations ?? this.fontVariations, |
| decoration: decoration ?? this.decoration, |
| decorationColor: decorationColor ?? this.decorationColor, |
| decorationStyle: decorationStyle ?? this.decorationStyle, |
| decorationThickness: decorationThickness ?? this.decorationThickness, |
| debugLabel: newDebugLabel, |
| fontFamily: fontFamily ?? _fontFamily, |
| fontFamilyFallback: fontFamilyFallback ?? _fontFamilyFallback, |
| package: package ?? _package, |
| overflow: overflow ?? this.overflow, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Creates a copy of this text style replacing or altering the specified |
| /// properties. |
| /// |
| /// The non-numeric properties [color], [fontFamily], [decoration], |
| /// [decorationColor] and [decorationStyle] are replaced with the new values. |
| /// |
| /// [foreground] will be given preference over [color] if it is not null and |
| /// [background] will be given preference over [backgroundColor] if it is not |
| /// null. |
| /// |
| /// The numeric properties are multiplied by the given factors and then |
| /// incremented by the given deltas. |
| /// |
| /// For example, `style.apply(fontSizeFactor: 2.0, fontSizeDelta: 1.0)` would |
| /// return a [TextStyle] whose [fontSize] is `style.fontSize * 2.0 + 1.0`. |
| /// |
| /// For the [fontWeight], the delta is applied to the [FontWeight] enum index |
| /// values, so that for instance `style.apply(fontWeightDelta: -2)` when |
| /// applied to a `style` whose [fontWeight] is [FontWeight.w500] will return a |
| /// [TextStyle] with a [FontWeight.w300]. |
| /// |
| /// If the underlying values are null, then the corresponding factors and/or |
| /// deltas must not be specified. |
| /// |
| /// If [foreground] is specified on this object, then applying [color] here |
| /// will have no effect and if [background] is specified on this object, then |
| /// applying [backgroundColor] here will have no effect either. |
| TextStyle apply({ |
| Color? color, |
| Color? backgroundColor, |
| TextDecoration? decoration, |
| Color? decorationColor, |
| TextDecorationStyle? decorationStyle, |
| double decorationThicknessFactor = 1.0, |
| double decorationThicknessDelta = 0.0, |
| String? fontFamily, |
| List<String>? fontFamilyFallback, |
| double fontSizeFactor = 1.0, |
| double fontSizeDelta = 0.0, |
| int fontWeightDelta = 0, |
| FontStyle? fontStyle, |
| double letterSpacingFactor = 1.0, |
| double letterSpacingDelta = 0.0, |
| double wordSpacingFactor = 1.0, |
| double wordSpacingDelta = 0.0, |
| double heightFactor = 1.0, |
| double heightDelta = 0.0, |
| TextBaseline? textBaseline, |
| TextLeadingDistribution? leadingDistribution, |
| Locale? locale, |
| List<Shadow>? shadows, |
| List<FontFeature>? fontFeatures, |
| List<FontVariation>? fontVariations, |
| String? package, |
| TextOverflow? overflow, |
| }) { |
| assert(fontSize != null || (fontSizeFactor == 1.0 && fontSizeDelta == 0.0)); |
| assert(fontWeight != null || fontWeightDelta == 0.0); |
| assert(letterSpacing != null || (letterSpacingFactor == 1.0 && letterSpacingDelta == 0.0)); |
| assert(wordSpacing != null || (wordSpacingFactor == 1.0 && wordSpacingDelta == 0.0)); |
| assert(decorationThickness != null || (decorationThicknessFactor == 1.0 && decorationThicknessDelta == 0.0)); |
| |
| String? modifiedDebugLabel; |
| assert(() { |
| if (debugLabel != null) { |
| modifiedDebugLabel = '($debugLabel).apply'; |
| } |
| return true; |
| }()); |
| |
| return TextStyle( |
| inherit: inherit, |
| color: foreground == null ? color ?? this.color : null, |
| backgroundColor: background == null ? backgroundColor ?? this.backgroundColor : null, |
| fontFamily: fontFamily ?? _fontFamily, |
| fontFamilyFallback: fontFamilyFallback ?? _fontFamilyFallback, |
| fontSize: fontSize == null ? null : fontSize! * fontSizeFactor + fontSizeDelta, |
| fontWeight: fontWeight == null ? null : FontWeight.values[(fontWeight!.index + fontWeightDelta).clamp(0, FontWeight.values.length - 1)], // ignore_clamp_double_lint |
| fontStyle: fontStyle ?? this.fontStyle, |
| letterSpacing: letterSpacing == null ? null : letterSpacing! * letterSpacingFactor + letterSpacingDelta, |
| wordSpacing: wordSpacing == null ? null : wordSpacing! * wordSpacingFactor + wordSpacingDelta, |
| textBaseline: textBaseline ?? this.textBaseline, |
| height: height == null ? null : height! * heightFactor + heightDelta, |
| leadingDistribution: leadingDistribution ?? this.leadingDistribution, |
| locale: locale ?? this.locale, |
| foreground: foreground, |
| background: background, |
| shadows: shadows ?? this.shadows, |
| fontFeatures: fontFeatures ?? this.fontFeatures, |
| fontVariations: fontVariations ?? this.fontVariations, |
| decoration: decoration ?? this.decoration, |
| decorationColor: decorationColor ?? this.decorationColor, |
| decorationStyle: decorationStyle ?? this.decorationStyle, |
| decorationThickness: decorationThickness == null ? null : decorationThickness! * decorationThicknessFactor + decorationThicknessDelta, |
| overflow: overflow ?? this.overflow, |
| package: package ?? _package, |
| debugLabel: modifiedDebugLabel, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Returns a new text style that is a combination of this style and the given |
| /// [other] style. |
| /// |
| /// If the given [other] text style has its [TextStyle.inherit] set to true, |
| /// its null properties are replaced with the non-null properties of this text |
| /// style. The [other] style _inherits_ the properties of this style. Another |
| /// way to think of it is that the "missing" properties of the [other] style |
| /// are _filled_ by the properties of this style. |
| /// |
| /// If the given [other] text style has its [TextStyle.inherit] set to false, |
| /// returns the given [other] style unchanged. The [other] style does not |
| /// inherit properties of this style. |
| /// |
| /// If the given text style is null, returns this text style. |
| /// |
| /// One of [color] or [foreground] must be null, and if this or `other` has |
| /// [foreground] specified it will be given preference over any color parameter. |
| /// |
| /// Similarly, one of [backgroundColor] or [background] must be null, and if |
| /// this or `other` has [background] specified it will be given preference |
| /// over any backgroundColor parameter. |
| TextStyle merge(TextStyle? other) { |
| if (other == null) { |
| return this; |
| } |
| if (!other.inherit) { |
| return other; |
| } |
| |
| String? mergedDebugLabel; |
| assert(() { |
| if (other.debugLabel != null || debugLabel != null) { |
| mergedDebugLabel = '(${debugLabel ?? _kDefaultDebugLabel}).merge(${other.debugLabel ?? _kDefaultDebugLabel})'; |
| } |
| return true; |
| }()); |
| |
| return copyWith( |
| color: other.color, |
| backgroundColor: other.backgroundColor, |
| fontSize: other.fontSize, |
| fontWeight: other.fontWeight, |
| fontStyle: other.fontStyle, |
| letterSpacing: other.letterSpacing, |
| wordSpacing: other.wordSpacing, |
| textBaseline: other.textBaseline, |
| height: other.height, |
| leadingDistribution: other.leadingDistribution, |
| locale: other.locale, |
| foreground: other.foreground, |
| background: other.background, |
| shadows: other.shadows, |
| fontFeatures: other.fontFeatures, |
| fontVariations: other.fontVariations, |
| decoration: other.decoration, |
| decorationColor: other.decorationColor, |
| decorationStyle: other.decorationStyle, |
| decorationThickness: other.decorationThickness, |
| debugLabel: mergedDebugLabel, |
| fontFamily: other._fontFamily, |
| fontFamilyFallback: other._fontFamilyFallback, |
| package: other._package, |
| overflow: other.overflow, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Interpolate between two text styles for animated transitions. |
| /// |
| /// Interpolation will not work well if the styles don't specify the same fields. |
| /// When this happens, to keep the interpolated transition smooth, the |
| /// implementation uses the non-null value throughout the transition for |
| /// lerpable fields such as colors (for example, if one [TextStyle] specified |
| /// `fontSize` but the other didn't, the returned [TextStyle] will use the |
| /// `fontSize` from the [TextStyle] that specified it, regardless of the `t` |
| /// value). |
| /// |
| /// This method throws when the given [TextStyle]s don't have the same |
| /// [inherit] value and a lerpable field is missing from both [TextStyle]s, |
| /// as that could result in jumpy transitions. |
| /// |
| /// {@macro dart.ui.shadow.lerp} |
| /// |
| /// If [foreground] is specified on either of `a` or `b`, both will be treated |
| /// as if they have a [foreground] paint (creating a new [Paint] if necessary |
| /// based on the [color] property). |
| /// |
| /// If [background] is specified on either of `a` or `b`, both will be treated |
| /// as if they have a [background] paint (creating a new [Paint] if necessary |
| /// based on the [backgroundColor] property). |
| static TextStyle? lerp(TextStyle? a, TextStyle? b, double t) { |
| if (identical(a, b)) { |
| return a; |
| } |
| String? lerpDebugLabel; |
| assert(() { |
| lerpDebugLabel = 'lerp(${a?.debugLabel ?? _kDefaultDebugLabel} ⎯${t.toStringAsFixed(1)}→ ${b?.debugLabel ?? _kDefaultDebugLabel})'; |
| return true; |
| }()); |
| |
| if (a == null) { |
| return TextStyle( |
| inherit: b!.inherit, |
| color: Color.lerp(null, b.color, t), |
| backgroundColor: Color.lerp(null, b.backgroundColor, t), |
| fontSize: t < 0.5 ? null : b.fontSize, |
| fontWeight: FontWeight.lerp(null, b.fontWeight, t), |
| fontStyle: t < 0.5 ? null : b.fontStyle, |
| letterSpacing: t < 0.5 ? null : b.letterSpacing, |
| wordSpacing: t < 0.5 ? null : b.wordSpacing, |
| textBaseline: t < 0.5 ? null : b.textBaseline, |
| height: t < 0.5 ? null : b.height, |
| leadingDistribution: t < 0.5 ? null : b.leadingDistribution, |
| locale: t < 0.5 ? null : b.locale, |
| foreground: t < 0.5 ? null : b.foreground, |
| background: t < 0.5 ? null : b.background, |
| shadows: t < 0.5 ? null : b.shadows, |
| fontFeatures: t < 0.5 ? null : b.fontFeatures, |
| fontVariations: lerpFontVariations(null, b.fontVariations, t), |
| decoration: t < 0.5 ? null : b.decoration, |
| decorationColor: Color.lerp(null, b.decorationColor, t), |
| decorationStyle: t < 0.5 ? null : b.decorationStyle, |
| decorationThickness: t < 0.5 ? null : b.decorationThickness, |
| debugLabel: lerpDebugLabel, |
| fontFamily: t < 0.5 ? null : b._fontFamily, |
| fontFamilyFallback: t < 0.5 ? null : b._fontFamilyFallback, |
| package: t < 0.5 ? null : b._package, |
| overflow: t < 0.5 ? null : b.overflow, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| if (b == null) { |
| return TextStyle( |
| inherit: a.inherit, |
| color: Color.lerp(a.color, null, t), |
| backgroundColor: Color.lerp(null, a.backgroundColor, t), |
| fontSize: t < 0.5 ? a.fontSize : null, |
| fontWeight: FontWeight.lerp(a.fontWeight, null, t), |
| fontStyle: t < 0.5 ? a.fontStyle : null, |
| letterSpacing: t < 0.5 ? a.letterSpacing : null, |
| wordSpacing: t < 0.5 ? a.wordSpacing : null, |
| textBaseline: t < 0.5 ? a.textBaseline : null, |
| height: t < 0.5 ? a.height : null, |
| leadingDistribution: t < 0.5 ? a.leadingDistribution : null, |
| locale: t < 0.5 ? a.locale : null, |
| foreground: t < 0.5 ? a.foreground : null, |
| background: t < 0.5 ? a.background : null, |
| shadows: t < 0.5 ? a.shadows : null, |
| fontFeatures: t < 0.5 ? a.fontFeatures : null, |
| fontVariations: lerpFontVariations(a.fontVariations, null, t), |
| decoration: t < 0.5 ? a.decoration : null, |
| decorationColor: Color.lerp(a.decorationColor, null, t), |
| decorationStyle: t < 0.5 ? a.decorationStyle : null, |
| decorationThickness: t < 0.5 ? a.decorationThickness : null, |
| debugLabel: lerpDebugLabel, |
| fontFamily: t < 0.5 ? a._fontFamily : null, |
| fontFamilyFallback: t < 0.5 ? a._fontFamilyFallback : null, |
| package: t < 0.5 ? a._package : null, |
| overflow: t < 0.5 ? a.overflow : null, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| assert(() { |
| if (a.inherit == b.inherit) { |
| return true; |
| } |
| |
| final List<String> nullFields = <String>[ |
| if (a.foreground == null && b.foreground == null && a.color == null && b.color == null) 'color', |
| if (a.background == null && b.background == null && a.backgroundColor == null && b.backgroundColor == null) 'backgroundColor', |
| if (a.fontSize == null && b.fontSize == null) 'fontSize', |
| if (a.letterSpacing == null && b.letterSpacing == null) 'letterSpacing', |
| if (a.wordSpacing == null && b.wordSpacing == null) 'wordSpacing', |
| if (a.height == null && b.height == null) 'height', |
| if (a.decorationColor == null && b.decorationColor == null) 'decorationColor', |
| if (a.decorationThickness == null && b.decorationThickness == null) 'decorationThickness', |
| ]; |
| if (nullFields.isEmpty) { |
| return true; |
| } |
| |
| throw FlutterError.fromParts(<DiagnosticsNode>[ |
| ErrorSummary('Failed to interpolate TextStyles with different inherit values.'), |
| ErrorSpacer(), |
| ErrorDescription('The TextStyles being interpolated were:'), |
| a.toDiagnosticsNode(name: 'from', style: DiagnosticsTreeStyle.singleLine), |
| b.toDiagnosticsNode(name: 'to', style: DiagnosticsTreeStyle.singleLine), |
| ErrorDescription( |
| 'The following fields are unspecified in both TextStyles:\n' |
| '${nullFields.map((String name) => '"$name"').join(', ')}.\n' |
| 'When "inherit" changes during the transition, these fields may ' |
| 'observe abrupt value changes as a result, causing "jump"s in the ' |
| 'transition.' |
| ), |
| ErrorSpacer(), |
| ErrorHint( |
| 'In general, TextStyle.lerp only works well when both TextStyles have ' |
| 'the same "inherit" value, and specify the same fields.', |
| ), |
| ErrorHint( |
| 'If the TextStyles were directly created by you, consider bringing ' |
| 'them to parity to ensure a smooth transition.' |
| ), |
| ErrorSpacer(), |
| ErrorHint( |
| 'If one of the TextStyles being lerped is significantly more elaborate ' |
| 'than the other, and has "inherited" set to false, it is often because ' |
| 'it is merged with another TextStyle before being lerped. Comparing ' |
| 'the "debugLabel"s of the two TextStyles may help identify if that was ' |
| 'the case.' |
| ), |
| ErrorHint( |
| 'For example, you may see this error message when trying to lerp ' |
| 'between "ThemeData()" and "Theme.of(context)". This is because ' |
| 'TextStyles from "Theme.of(context)" are merged with TextStyles from ' |
| 'another theme and thus are more elaborate than the TextStyles from ' |
| '"ThemeData()" (which is reflected in their "debugLabel"s -- ' |
| 'TextStyles from "Theme.of(context)" should have labels in the form of ' |
| '"(<A TextStyle>).merge(<Another TextStyle>)"). It is recommended to ' |
| 'only lerp ThemeData with matching TextStyles.' |
| ), |
| ]); |
| }()); |
| |
| return TextStyle( |
| inherit: t < 0.5 ? a.inherit : b.inherit, |
| color: a.foreground == null && b.foreground == null ? Color.lerp(a.color, b.color, t) : null, |
| backgroundColor: a.background == null && b.background == null ? Color.lerp(a.backgroundColor, b.backgroundColor, t) : null, |
| fontSize: ui.lerpDouble(a.fontSize ?? b.fontSize, b.fontSize ?? a.fontSize, t), |
| fontWeight: FontWeight.lerp(a.fontWeight, b.fontWeight, t), |
| fontStyle: t < 0.5 ? a.fontStyle : b.fontStyle, |
| letterSpacing: ui.lerpDouble(a.letterSpacing ?? b.letterSpacing, b.letterSpacing ?? a.letterSpacing, t), |
| wordSpacing: ui.lerpDouble(a.wordSpacing ?? b.wordSpacing, b.wordSpacing ?? a.wordSpacing, t), |
| textBaseline: t < 0.5 ? a.textBaseline : b.textBaseline, |
| height: ui.lerpDouble(a.height ?? b.height, b.height ?? a.height, t), |
| leadingDistribution: t < 0.5 ? a.leadingDistribution : b.leadingDistribution, |
| locale: t < 0.5 ? a.locale : b.locale, |
| foreground: (a.foreground != null || b.foreground != null) |
| ? t < 0.5 |
| ? a.foreground ?? (Paint()..color = a.color!) |
| : b.foreground ?? (Paint()..color = b.color!) |
| : null, |
| background: (a.background != null || b.background != null) |
| ? t < 0.5 |
| ? a.background ?? (Paint()..color = a.backgroundColor!) |
| : b.background ?? (Paint()..color = b.backgroundColor!) |
| : null, |
| shadows: t < 0.5 ? a.shadows : b.shadows, |
| fontFeatures: t < 0.5 ? a.fontFeatures : b.fontFeatures, |
| fontVariations: lerpFontVariations(a.fontVariations, b.fontVariations, t), |
| decoration: t < 0.5 ? a.decoration : b.decoration, |
| decorationColor: Color.lerp(a.decorationColor, b.decorationColor, t), |
| decorationStyle: t < 0.5 ? a.decorationStyle : b.decorationStyle, |
| decorationThickness: ui.lerpDouble(a.decorationThickness ?? b.decorationThickness, b.decorationThickness ?? a.decorationThickness, t), |
| debugLabel: lerpDebugLabel, |
| fontFamily: t < 0.5 ? a._fontFamily : b._fontFamily, |
| fontFamilyFallback: t < 0.5 ? a._fontFamilyFallback : b._fontFamilyFallback, |
| package: t < 0.5 ? a._package : b._package, |
| overflow: t < 0.5 ? a.overflow : b.overflow, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// The style information for text runs, encoded for use by `dart:ui`. |
| ui.TextStyle getTextStyle({ |
| @Deprecated( |
| 'Use textScaler instead. ' |
| 'Use of textScaleFactor was deprecated in preparation for the upcoming nonlinear text scaling support. ' |
| 'This feature was deprecated after v3.12.0-2.0.pre.', |
| ) |
| double textScaleFactor = 1.0, |
| TextScaler textScaler = TextScaler.noScaling, |
| }) { |
| assert( |
| identical(textScaler, TextScaler.noScaling) || textScaleFactor == 1.0, |
| 'textScaleFactor is deprecated and cannot be specified when textScaler is specified.', |
| ); |
| final double? fontSize = switch (this.fontSize) { |
| null => null, |
| final double size when textScaler == TextScaler.noScaling => size * textScaleFactor, |
| final double size => textScaler.scale(size), |
| }; |
| return ui.TextStyle( |
| color: color, |
| decoration: decoration, |
| decorationColor: decorationColor, |
| decorationStyle: decorationStyle, |
| decorationThickness: decorationThickness, |
| fontWeight: fontWeight, |
| fontStyle: fontStyle, |
| textBaseline: textBaseline, |
| leadingDistribution: leadingDistribution, |
| fontFamily: fontFamily, |
| fontFamilyFallback: fontFamilyFallback, |
| fontSize: fontSize, |
| letterSpacing: letterSpacing, |
| wordSpacing: wordSpacing, |
| height: height, |
| locale: locale, |
| foreground: foreground, |
| background: switch ((background, backgroundColor)) { |
| (final Paint paint, _) => paint, |
| (_, final Color color) => Paint()..color = color, |
| _ => null, |
| }, |
| shadows: shadows, |
| fontFeatures: fontFeatures, |
| fontVariations: fontVariations, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// The style information for paragraphs, encoded for use by `dart:ui`. |
| /// |
| /// If the `textScaleFactor` argument is omitted, it defaults to one. The |
| /// other arguments may be null. The `maxLines` argument, if specified and |
| /// non-null, must be greater than zero. |
| /// |
| /// If the font size on this style isn't set, it will default to 14 logical |
| /// pixels. |
| ui.ParagraphStyle getParagraphStyle({ |
| TextAlign? textAlign, |
| TextDirection? textDirection, |
| TextScaler textScaler = TextScaler.noScaling, |
| String? ellipsis, |
| int? maxLines, |
| TextHeightBehavior? textHeightBehavior, |
| Locale? locale, |
| String? fontFamily, |
| double? fontSize, |
| FontWeight? fontWeight, |
| FontStyle? fontStyle, |
| double? height, |
| StrutStyle? strutStyle, |
| }) { |
| assert(maxLines == null || maxLines > 0); |
| final TextLeadingDistribution? leadingDistribution = this.leadingDistribution; |
| final TextHeightBehavior? effectiveTextHeightBehavior = textHeightBehavior |
| ?? (leadingDistribution == null ? null : TextHeightBehavior(leadingDistribution: leadingDistribution)); |
| |
| return ui.ParagraphStyle( |
| textAlign: textAlign, |
| textDirection: textDirection, |
| // Here, we establish the contents of this TextStyle as the paragraph's default font |
| // unless an override is passed in. |
| fontWeight: fontWeight ?? this.fontWeight, |
| fontStyle: fontStyle ?? this.fontStyle, |
| fontFamily: fontFamily ?? this.fontFamily, |
| fontSize: textScaler.scale(fontSize ?? this.fontSize ?? kDefaultFontSize), |
| height: height ?? this.height, |
| textHeightBehavior: effectiveTextHeightBehavior, |
| strutStyle: strutStyle == null ? null : ui.StrutStyle( |
| fontFamily: strutStyle.fontFamily, |
| fontFamilyFallback: strutStyle.fontFamilyFallback, |
| fontSize: switch (strutStyle.fontSize) { |
| null => null, |
| final double unscaled => textScaler.scale(unscaled), |
| }, |
| height: strutStyle.height, |
| leading: strutStyle.leading, |
| fontWeight: strutStyle.fontWeight, |
| fontStyle: strutStyle.fontStyle, |
| forceStrutHeight: strutStyle.forceStrutHeight, |
| ), |
| maxLines: maxLines, |
| ellipsis: ellipsis, |
| locale: locale, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| /// Describe the difference between this style and another, in terms of how |
| /// much damage it will make to the rendering. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [TextSpan.compareTo], which does the same thing for entire [TextSpan]s. |
| RenderComparison compareTo(TextStyle other) { |
| if (identical(this, other)) { |
| return RenderComparison.identical; |
| } |
| if (inherit != other.inherit || |
| fontFamily != other.fontFamily || |
| fontSize != other.fontSize || |
| fontWeight != other.fontWeight || |
| fontStyle != other.fontStyle || |
| letterSpacing != other.letterSpacing || |
| wordSpacing != other.wordSpacing || |
| textBaseline != other.textBaseline || |
| height != other.height || |
| leadingDistribution != other.leadingDistribution || |
| locale != other.locale || |
| foreground != other.foreground || |
| background != other.background || |
| !listEquals(shadows, other.shadows) || |
| !listEquals(fontFeatures, other.fontFeatures) || |
| !listEquals(fontVariations, other.fontVariations) || |
| !listEquals(fontFamilyFallback, other.fontFamilyFallback) || |
| overflow != other.overflow) { |
| return RenderComparison.layout; |
| } |
| if (color != other.color || |
| backgroundColor != other.backgroundColor || |
| decoration != other.decoration || |
| decorationColor != other.decorationColor || |
| decorationStyle != other.decorationStyle || |
| decorationThickness != other.decorationThickness) { |
| return RenderComparison.paint; |
| } |
| return RenderComparison.identical; |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| bool operator ==(Object other) { |
| if (identical(this, other)) { |
| return true; |
| } |
| if (other.runtimeType != runtimeType) { |
| return false; |
| } |
| return other is TextStyle |
| && other.inherit == inherit |
| && other.color == color |
| && other.backgroundColor == backgroundColor |
| && other.fontSize == fontSize |
| && other.fontWeight == fontWeight |
| && other.fontStyle == fontStyle |
| && other.letterSpacing == letterSpacing |
| && other.wordSpacing == wordSpacing |
| && other.textBaseline == textBaseline |
| && other.height == height |
| && other.leadingDistribution == leadingDistribution |
| && other.locale == locale |
| && other.foreground == foreground |
| && other.background == background |
| && listEquals(other.shadows, shadows) |
| && listEquals(other.fontFeatures, fontFeatures) |
| && listEquals(other.fontVariations, fontVariations) |
| && other.decoration == decoration |
| && other.decorationColor == decorationColor |
| && other.decorationStyle == decorationStyle |
| && other.decorationThickness == decorationThickness |
| && other.fontFamily == fontFamily |
| && listEquals(other.fontFamilyFallback, fontFamilyFallback) |
| && other._package == _package |
| && other.overflow == overflow; |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| int get hashCode { |
| final List<String>? fontFamilyFallback = this.fontFamilyFallback; |
| final int fontHash = Object.hash( |
| decorationStyle, |
| decorationThickness, |
| fontFamily, |
| fontFamilyFallback == null ? null : Object.hashAll(fontFamilyFallback), |
| _package, |
| overflow, |
| ); |
| |
| final List<Shadow>? shadows = this.shadows; |
| final List<FontFeature>? fontFeatures = this.fontFeatures; |
| final List<FontVariation>? fontVariations = this.fontVariations; |
| return Object.hash( |
| inherit, |
| color, |
| backgroundColor, |
| fontSize, |
| fontWeight, |
| fontStyle, |
| letterSpacing, |
| wordSpacing, |
| textBaseline, |
| height, |
| leadingDistribution, |
| locale, |
| foreground, |
| background, |
| shadows == null ? null : Object.hashAll(shadows), |
| fontFeatures == null ? null : Object.hashAll(fontFeatures), |
| fontVariations == null ? null : Object.hashAll(fontVariations), |
| decoration, |
| decorationColor, |
| fontHash, |
| ); |
| } |
| |
| @override |
| String toStringShort() => objectRuntimeType(this, 'TextStyle'); |
| |
| /// Adds all properties prefixing property names with the optional `prefix`. |
| @override |
| void debugFillProperties(DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties, { String prefix = '' }) { |
| super.debugFillProperties(properties); |
| if (debugLabel != null) { |
| properties.add(MessageProperty('${prefix}debugLabel', debugLabel!)); |
| } |
| final List<DiagnosticsNode> styles = <DiagnosticsNode>[ |
| ColorProperty('${prefix}color', color, defaultValue: null), |
| ColorProperty('${prefix}backgroundColor', backgroundColor, defaultValue: null), |
| StringProperty('${prefix}family', fontFamily, defaultValue: null, quoted: false), |
| IterableProperty<String>('${prefix}familyFallback', fontFamilyFallback, defaultValue: null), |
| DoubleProperty('${prefix}size', fontSize, defaultValue: null), |
| ]; |
| String? weightDescription; |
| if (fontWeight != null) { |
| weightDescription = '${fontWeight!.index + 1}00'; |
| } |
| // TODO(jacobr): switch this to use enumProperty which will either cause the |
| // weight description to change to w600 from 600 or require existing |
| // enumProperty to handle this special case. |
| styles.add(DiagnosticsProperty<FontWeight>( |
| '${prefix}weight', |
| fontWeight, |
| description: weightDescription, |
| defaultValue: null, |
| )); |
| styles.add(EnumProperty<FontStyle>('${prefix}style', fontStyle, defaultValue: null)); |
| styles.add(DoubleProperty('${prefix}letterSpacing', letterSpacing, defaultValue: null)); |
| styles.add(DoubleProperty('${prefix}wordSpacing', wordSpacing, defaultValue: null)); |
| styles.add(EnumProperty<TextBaseline>('${prefix}baseline', textBaseline, defaultValue: null)); |
| styles.add(DoubleProperty('${prefix}height', height, unit: 'x', defaultValue: null)); |
| styles.add(EnumProperty<TextLeadingDistribution>('${prefix}leadingDistribution', leadingDistribution, defaultValue: null)); |
| styles.add(DiagnosticsProperty<Locale>('${prefix}locale', locale, defaultValue: null)); |
| styles.add(DiagnosticsProperty<Paint>('${prefix}foreground', foreground, defaultValue: null)); |
| styles.add(DiagnosticsProperty<Paint>('${prefix}background', background, defaultValue: null)); |
| if (decoration != null || decorationColor != null || decorationStyle != null || decorationThickness != null) { |
| final List<String> decorationDescription = <String>[]; |
| if (decorationStyle != null) { |
| decorationDescription.add(decorationStyle!.name); |
| } |
| |
| // Hide decorationColor from the default text view as it is shown in the |
| // terse decoration summary as well. |
| styles.add(ColorProperty('${prefix}decorationColor', decorationColor, defaultValue: null, level: DiagnosticLevel.fine)); |
| |
| if (decorationColor != null) { |
| decorationDescription.add('$decorationColor'); |
| } |
| |
| // Intentionally collide with the property 'decoration' added below. |
| // Tools that show hidden properties could choose the first property |
| // matching the name to disambiguate. |
| styles.add(DiagnosticsProperty<TextDecoration>('${prefix}decoration', decoration, defaultValue: null, level: DiagnosticLevel.hidden)); |
| if (decoration != null) { |
| decorationDescription.add('$decoration'); |
| } |
| assert(decorationDescription.isNotEmpty); |
| styles.add(MessageProperty('${prefix}decoration', decorationDescription.join(' '))); |
| styles.add(DoubleProperty('${prefix}decorationThickness', decorationThickness, unit: 'x', defaultValue: null)); |
| } |
| |
| final bool styleSpecified = styles.any((DiagnosticsNode n) => !n.isFiltered(DiagnosticLevel.info)); |
| properties.add(DiagnosticsProperty<bool>('${prefix}inherit', inherit, level: (!styleSpecified && inherit) ? DiagnosticLevel.fine : DiagnosticLevel.info)); |
| styles.forEach(properties.add); |
| |
| if (!styleSpecified) { |
| properties.add(FlagProperty('inherit', value: inherit, ifTrue: '$prefix<all styles inherited>', ifFalse: '$prefix<no style specified>')); |
| } |
| |
| styles.add(EnumProperty<TextOverflow>('${prefix}overflow', overflow, defaultValue: null)); |
| } |
| } |
| |
| /// Interpolate between two lists of [FontVariation] objects. |
| /// |
| /// Variations are paired by axis, and interpolated using [FontVariation.lerp]. |
| /// |
| /// Entries that are only present in one list are animated using a step-function |
| /// at t=0.5 that enables or disables the variation. This can be jarring and |
| /// largely defeats the point of animating font variations. For best results, |
| /// specify the same axes in both lists, and for best performance, specify them |
| /// in the same order. |
| /// |
| /// ## Performance details |
| /// |
| /// This algorithm is O(N), but the constant factor varies based on the input, |
| /// and that is probably more important (because typically N is going to be |
| /// tiny, like 1 or 2; at the time of writing, there are only about five defined |
| /// axes that fonts typically use!). |
| /// |
| /// It is fastest when the lists contain the same axes ([FontVariation.axis]) in |
| /// the same order. The result is again in the same order, and no attempt is |
| /// made to detect or remove duplicates in this process. This is, by far, the |
| /// recommended way to use this algorithm. |
| /// |
| /// When the order of items in the two input lists vary, the constant factor |
| /// increases substantially, as it involves creating two maps and a set, |
| /// inserting every variation in both lists into the maps and the set, and then |
| /// iterating over them to recreate the list. |
| /// |
| /// In this case, the resulting order is arbitrary. Duplicates are dropped; in |
| /// each list, the last [FontVariation] for any particular axis is the one used |
| /// to compute the value for that axis. Values that only appear on one side are |
| /// interpolated using [FontVariation.lerp] against a null value, and resulting |
| /// null values are omitted from the resulting list. |
| /// |
| /// When the lists begin with matching pairs of axes, the fast algorithm is used |
| /// up to the point where the lists diverge, and the more expensive algorithm |
| /// is used on the remaining entries. |
| /// |
| /// See also: |
| /// |
| /// * [TextStyle.lerp], which uses this function to handle |
| /// [TextStyle.fontVariations]. |
| List<FontVariation>? lerpFontVariations(List<FontVariation>? a, List<FontVariation>? b, double t) { |
| if (t == 0.0) { |
| return a; |
| } |
| if (t == 1.0) { |
| return b; |
| } |
| if (a == null || a.isEmpty || b == null || b.isEmpty) { |
| // If one side is empty, that means anything on the other |
| // side will use the null-to-something lerp, which is to |
| // say, a step function at t=0.5. |
| return t < 0.5 ? a : b; |
| } |
| assert(a.isNotEmpty && b.isNotEmpty); |
| final List<FontVariation> result = <FontVariation>[]; |
| // First, try the efficient O(N) solution in the event that |
| // the lists are compatible. |
| int index = 0; |
| final int minLength = a.length < b.length ? a.length : b.length; |
| for (; index < minLength; index += 1) { |
| if (a[index].axis != b[index].axis) { |
| // The lists aren't compatible. |
| break; |
| } |
| result.add(FontVariation.lerp(a[index], b[index], t)!); |
| } |
| final int maxLength = a.length > b.length ? a.length : b.length; |
| if (index < maxLength) { |
| // If we get here, we have found some case where we cannot |
| // use the efficient approach. |
| final Set<String> axes = HashSet<String>(); |
| final Map<String, FontVariation> aVariations = HashMap<String, FontVariation>(); |
| for (int indexA = index; indexA < a.length; indexA += 1) { |
| aVariations[a[indexA].axis] = a[indexA]; |
| axes.add(a[indexA].axis); |
| } |
| final Map<String, FontVariation> bVariations = HashMap<String, FontVariation>(); |
| for (int indexB = index; indexB < b.length; indexB += 1) { |
| bVariations[b[indexB].axis] = b[indexB]; |
| axes.add(b[indexB].axis); |
| } |
| for (final String axis in axes) { |
| final FontVariation? variation = FontVariation.lerp(aVariations[axis], bVariations[axis], t); |
| if (variation != null) { |
| result.add(variation); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| return result; |
| } |